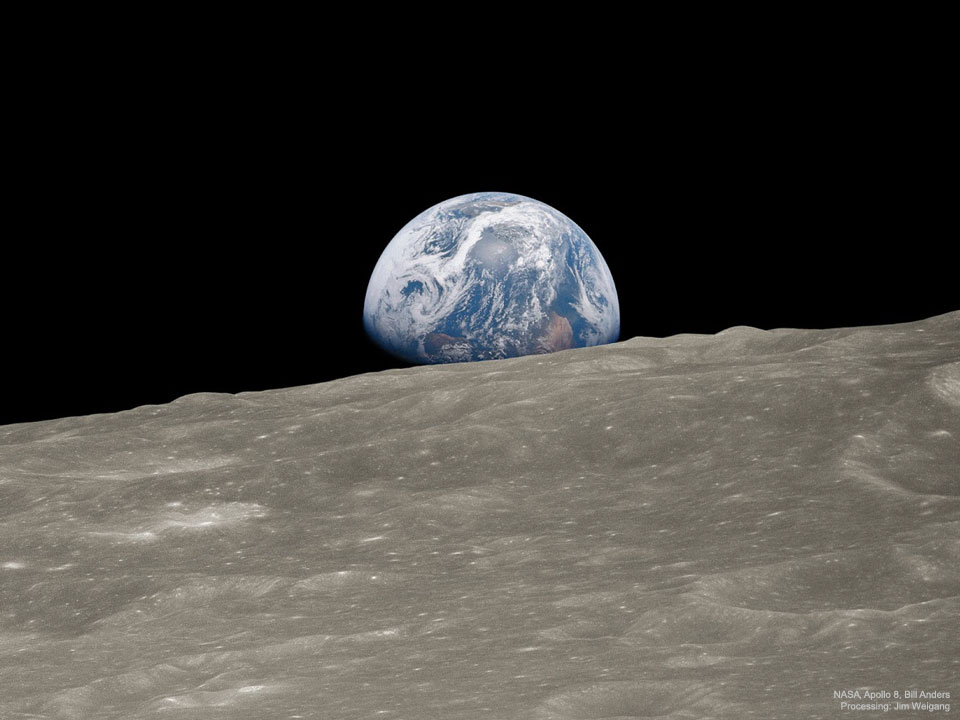
« Oh my God! Look at that picture over there! Here’s the Earth coming up. Wow is that pretty! » Soon after that pronouncement, 50 years ago today, one of the most famous images ever taken was snapped from the orbit of the Moon. Now known as « Earthrise », the iconic image shows the Earth rising above the limb of the Moon, as taken by the crew of Apollo 8. But the well-known Earthrise image was actually the second image taken of the Earth rising above the lunar limb — it was just the first in color. With modern digital technology, however, the real first Earthrise image — originally in black and white — has now been remastered to have the combined resolution and color of the first three images. Behold! The featured image is a close-up of the picture that Apollo 8 astronaut Bill Anders was talking about. Thanks to modern technology and human ingenuity, now we can all see it. (Historical note: A different historic black & white image of the Earth setting behind the lunar limb was taken by the robotic Lunar Orbiter 1 two years earlier.) via NASA https://ift.tt/M6wEmVP