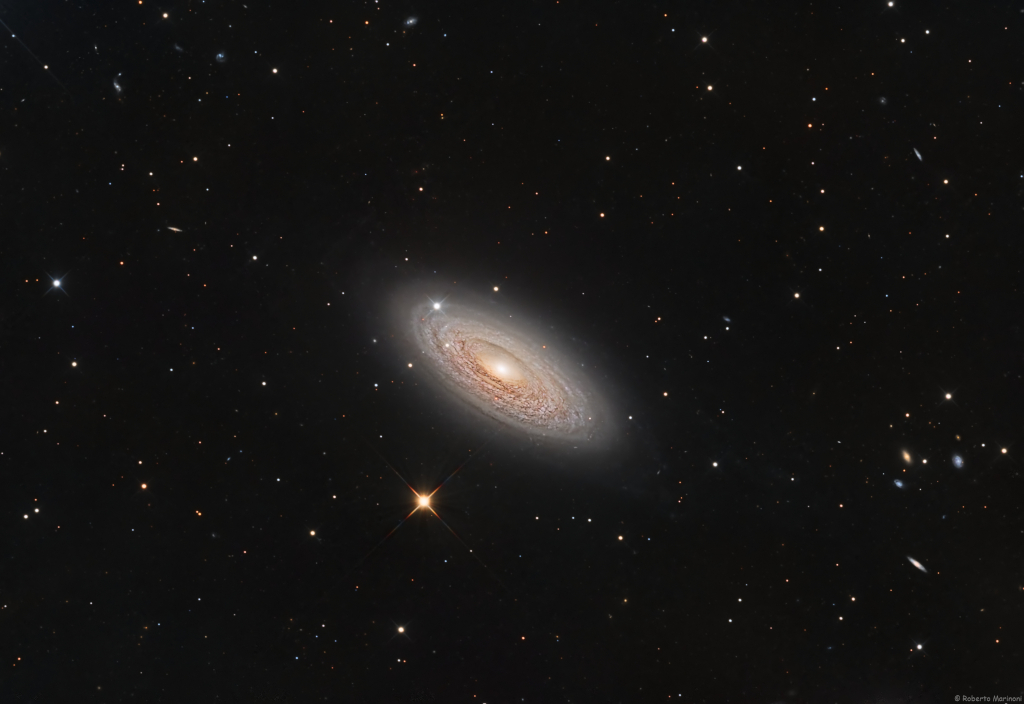
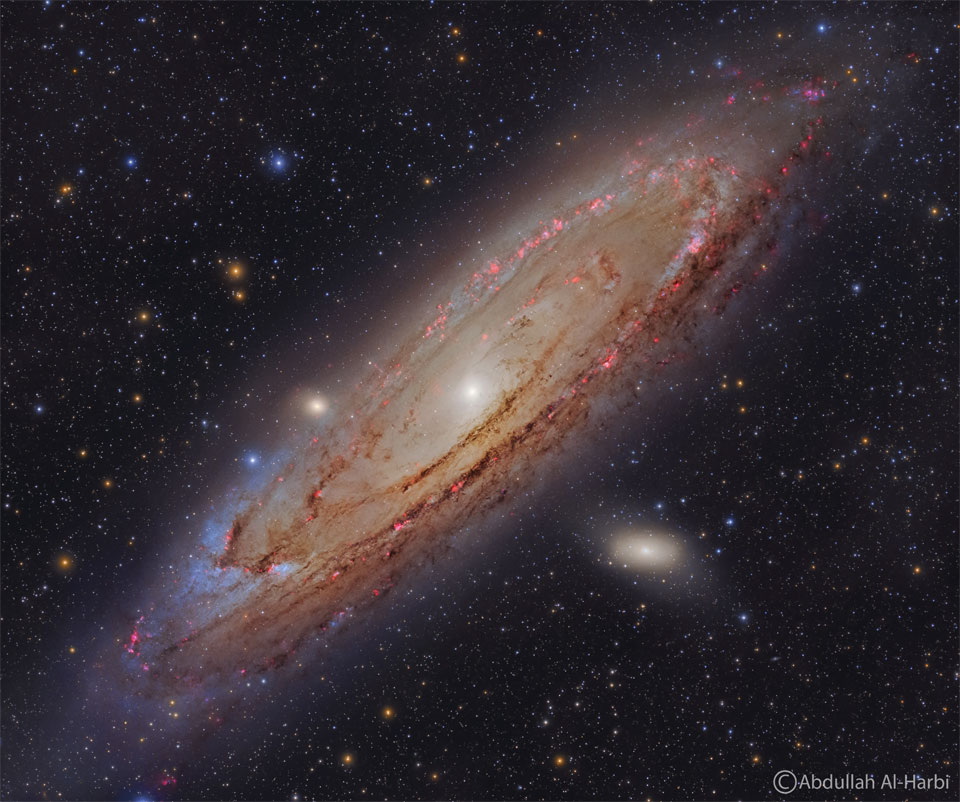
A mere 46 million light-years distant, spiral galaxy NGC 2841 can be found in planet Earth’s night sky toward the northern constellation of Ursa Major. This sharp image centered on the gorgeous island universe also captures spiky foreground Milky Way stars and more distant background galaxies within the same telescopic field of view. It shows off the bright nucleus of NGC 2841, along with its inclined galactic disk, and faint outer regions. Dust lanes, small star-forming regions, and young star clusters are embedded in the galaxy’s patchy, tightly wound spiral arms. In contrast, many other spirals exhibit broader, sweeping arms with large star-forming regions. NGC 2841 has a diameter of over 150,000 light-years, making it even larger than our own Milky Way. X-ray images suggest that extreme outflows from giant stars and stellar explosions create plumes of hot gas extending into a halo around NGC 2841. via NASA https://ift.tt/nIDfMZ1