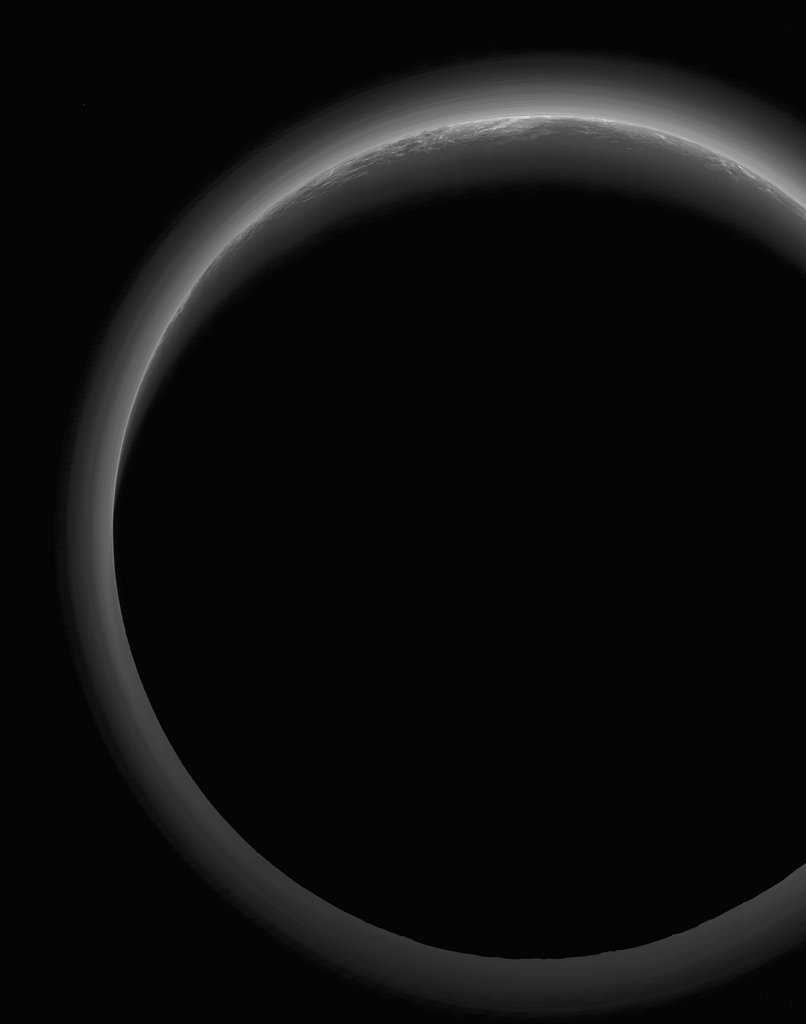
The night side of Pluto spans this shadowy scene. In the stunning spacebased perspective the Sun is 4.9 billion kilometers (almost 4.5 light-hours) behind the dim and distant world. It was captured by far flung New Horizons in July of 2015 when the spacecraft was at a range of some 21,000 kilometers from Pluto, about 19 minutes after its closest approach. A denizen of the Kuiper Belt in dramatic silhouette, the image also reveals Pluto’s tenuous, surprisingly complex layers of hazy atmosphere. Near the top of the frame the crescent twilight landscape includes southern areas of nitrogen ice plains now formally known as Sputnik Planitia and rugged mountains of water-ice in the Norgay Montes. via NASA https://ift.tt/c9FGAyJ