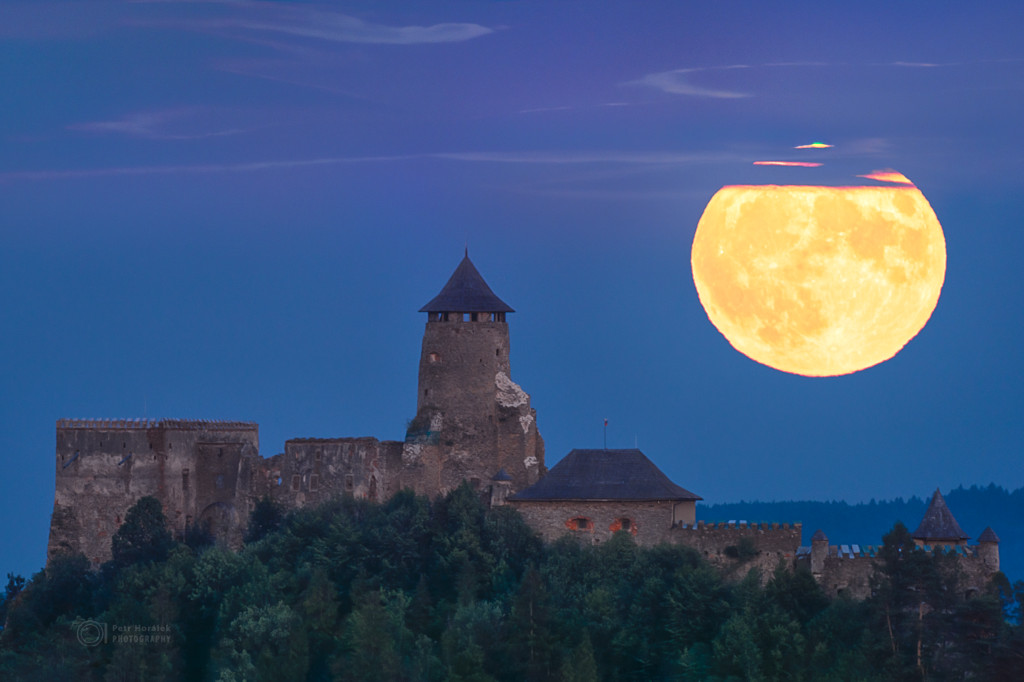
On July 13 this well-planned telephoto view recorded a Full Moon rising over Lubovna Castle in eastern Slovania. The photographer was about 3 kilometers from the castle walls and about 357,000 kilometers from this Full Moon near perigee, the closest point in its elliptical orbit. Known to some as supermoons, full moons near perigee are a little brighter and larger in planet Earth’s sky when compared to full moons that occur near the average lunar distance of around 384,000 kilometers. Of course any Full Moon near the horizon can show the effects of refraction over a long sight-line through dense clear atmosphere. In this image, atmospheric refraction creates the slight green flash framed by thin clouds near the top, with a ragged red rim along the bottom edge of July’s perigee Full Moon. via NASA https://ift.tt/jdn5Ey1