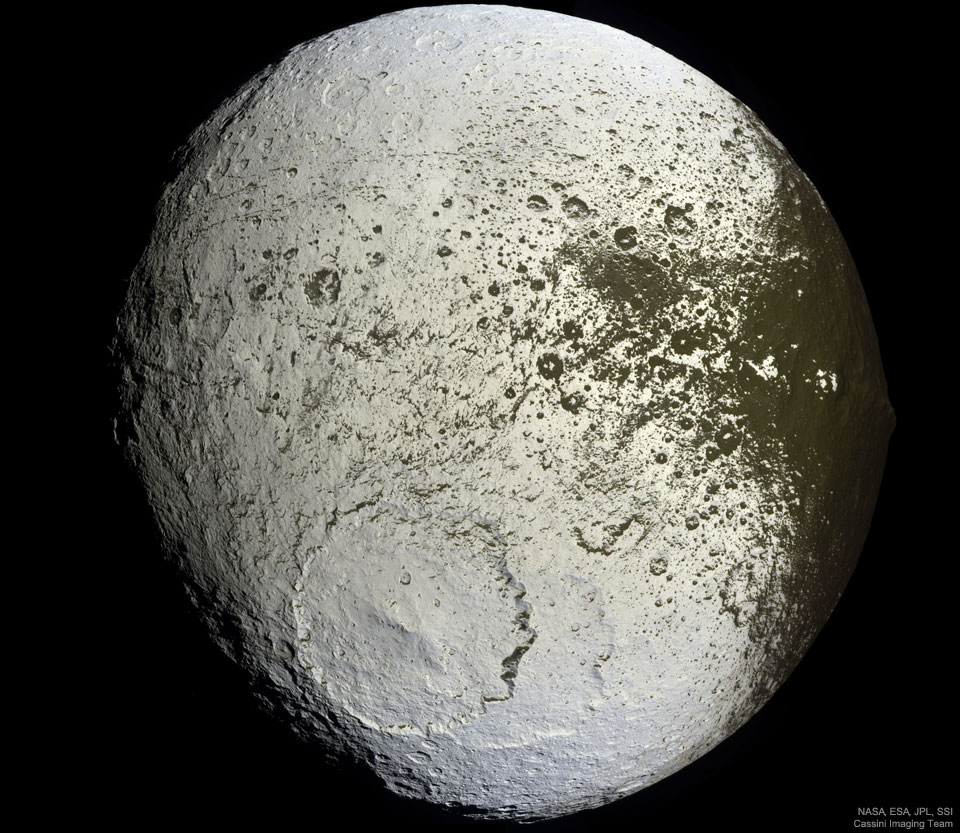
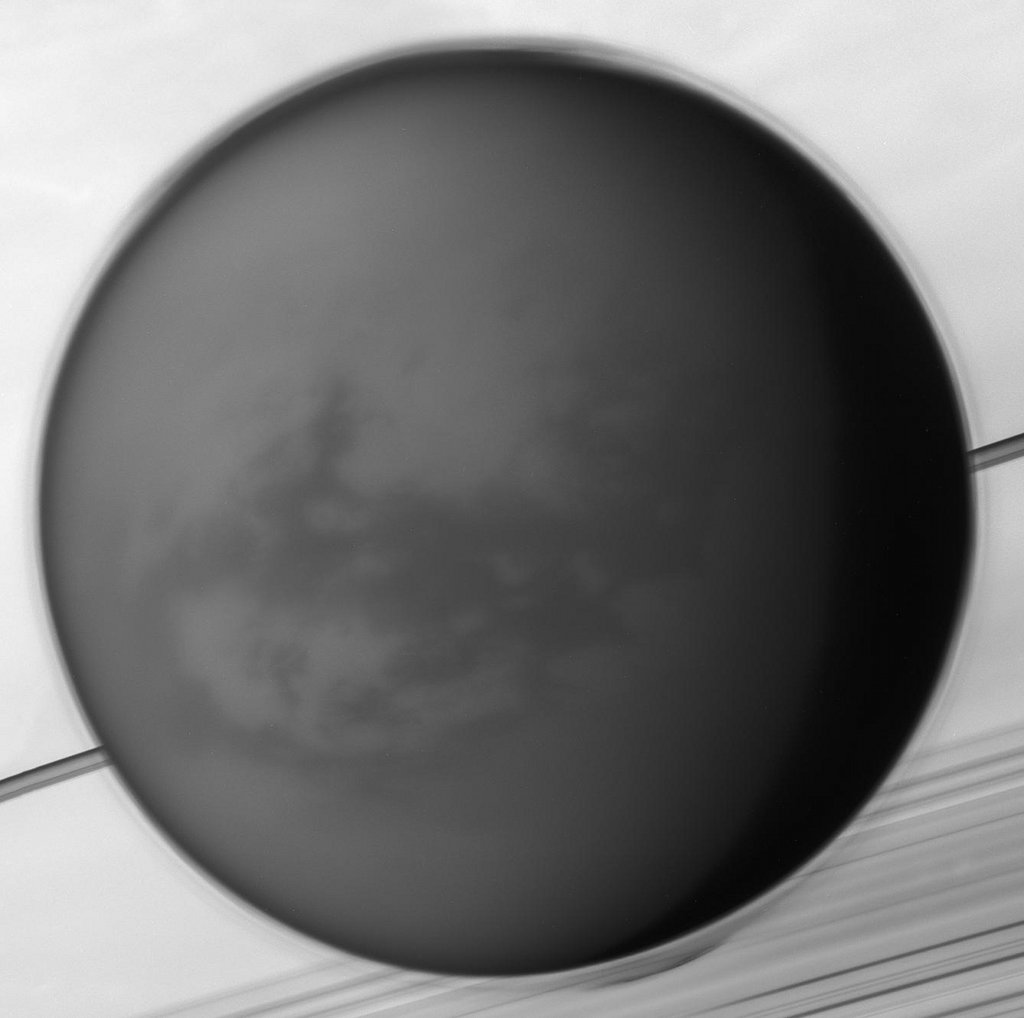
What has happened to Saturn’s moon Iapetus? Vast sections of this strange world are dark as coal, while others are as bright as ice. The composition of the dark material is unknown, but infrared spectra indicate that it possibly contains some dark form of carbon. Iapetus also has an unusual equatorial ridge that makes it appear like a walnut. To help better understand this seemingly painted moon, NASA directed the robotic Cassini spacecraft orbiting Saturn to swoop within 2,000 kilometers in 2007. Pictured here, from about 75,000 kilometers out, Cassini’s trajectory allowed unprecedented imaging of the hemisphere of Iapetus that is always trailing. A huge impact crater seen in the south spans a tremendous 450 kilometers and appears superposed on an older crater of similar size. The dark material is seen increasingly coating the easternmost part of Iapetus, darkening craters and highlands alike. Close inspection indicates that the dark coating typically faces the moon’s equator and is less than a meter thick. A leading hypothesis is that the dark material is mostly dirt leftover when relatively warm but dirty ice sublimates. An initial coating of dark material may have been effectively painted on by the accretion of meteor-liberated debris from other moons. via NASA https://ift.tt/2xCjmp1