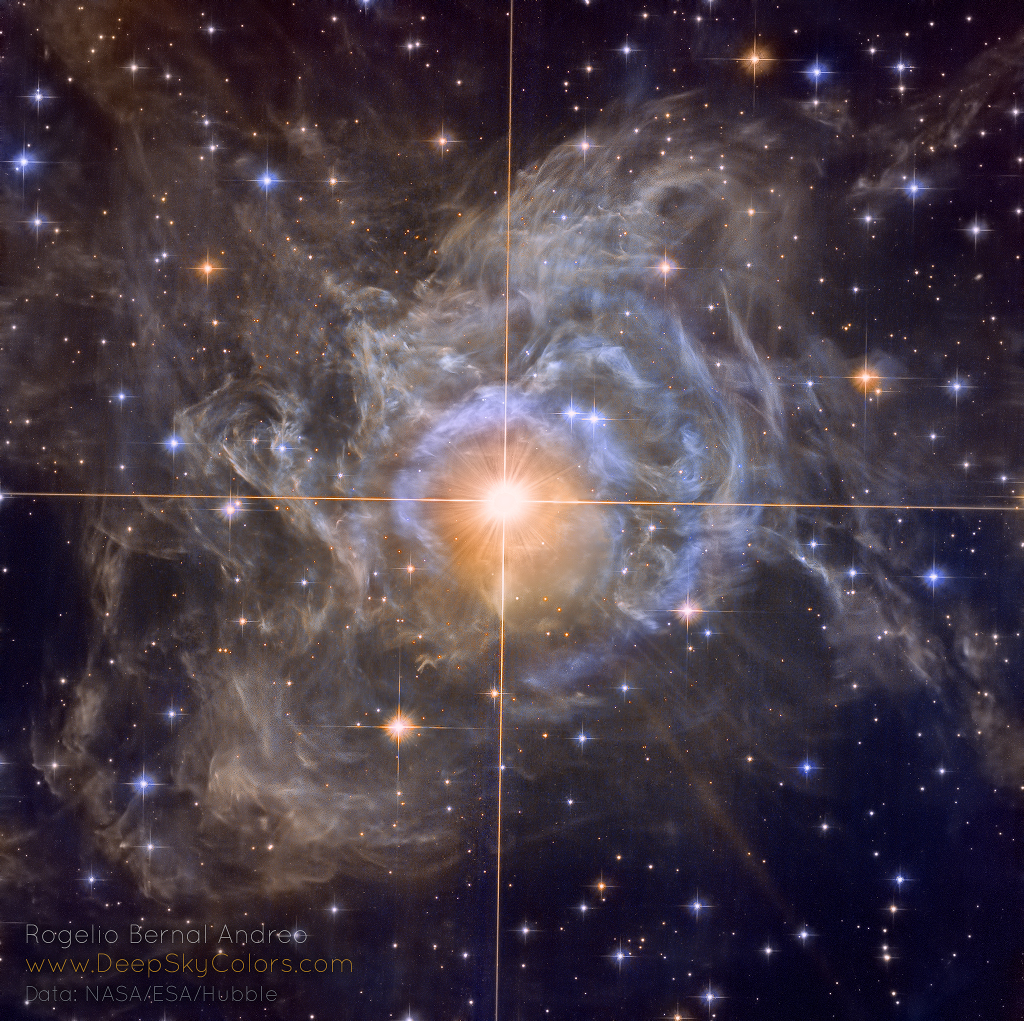
Pulsating RS Puppis, the brightest star in the image center, is some ten times more massive than our Sun and on average 15,000 times more luminous. In fact, RS Pup is a Cepheid variable star, a class of stars whose brightness is used to estimate distances to nearby galaxies as one of the first steps in establishing the cosmic distance scale. As RS Pup pulsates over a period of about 40 days, its regular changes in brightness are also seen along its surrounding nebula delayed in time, effectively a light echo. Using measurements of the time delay and angular size of the nebula, the known speed of light allows astronomers to geometrically determine the distance to RS Pup to be 6,500 light-years, with a remarkably small error of plus or minus 90 light-years. An impressive achievement for stellar astronomy, the echo-measured distance also more accurately establishes the true brightness of RS Pup, and by extension other Cepheid stars, improving the knowledge of distances to galaxies beyond the Milky Way. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2VGw7us