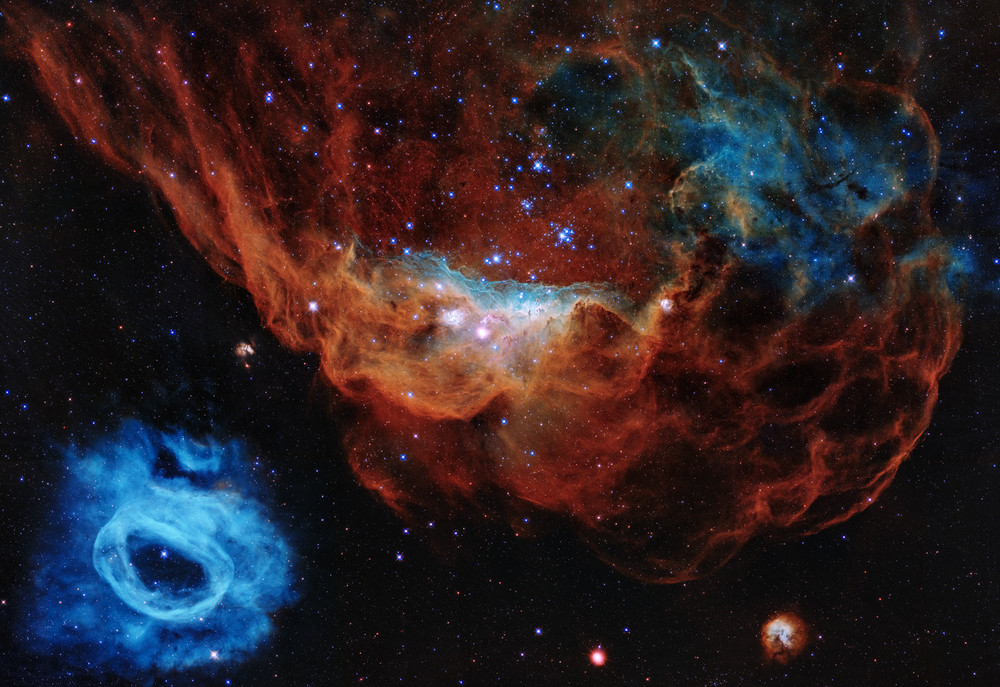
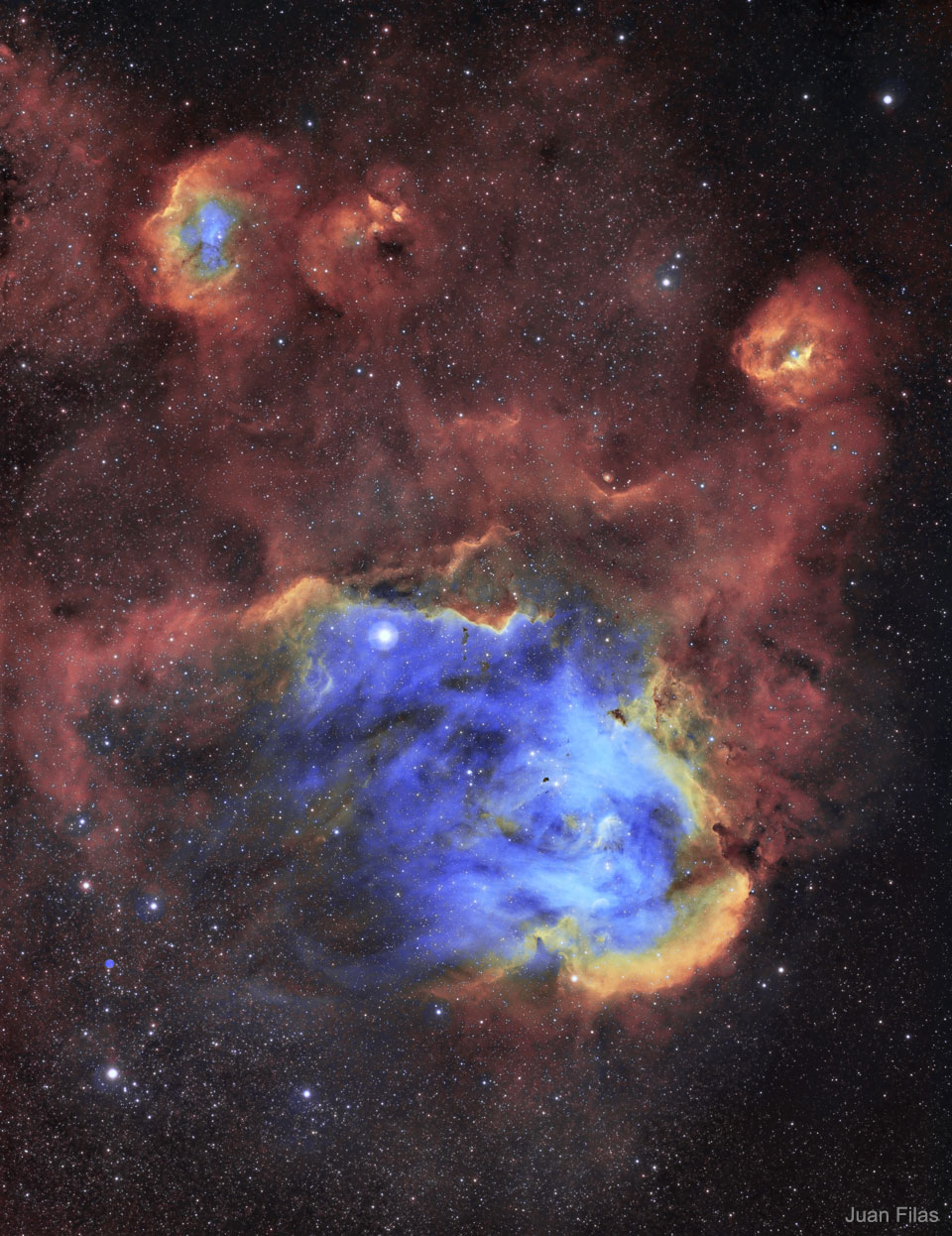
These bright ridges of interstellar gas and dust are bathed in energetic starlight. With its sea of young stars, the massive star-forming region NGC 2014 has been dubbed the Cosmic Reef. Drifting just off shore, the smaller NGC 2020, is an expansive blue-hued structure erupting from a single central Wolf-Rayet star, 200,000 times brighter than the Sun. The cosmic frame spans some 600 light-years within the Large Magellanic Cloud 160,000 light-years away, a satellite galaxy of our Milky Way. A magnificent Hubble Space Telescope portrait, the image was released this week as part of a celebration to mark Hubble’s 30th year exploring the Universe from Earth orbit. via NASA https://ift.tt/2S5DGqC