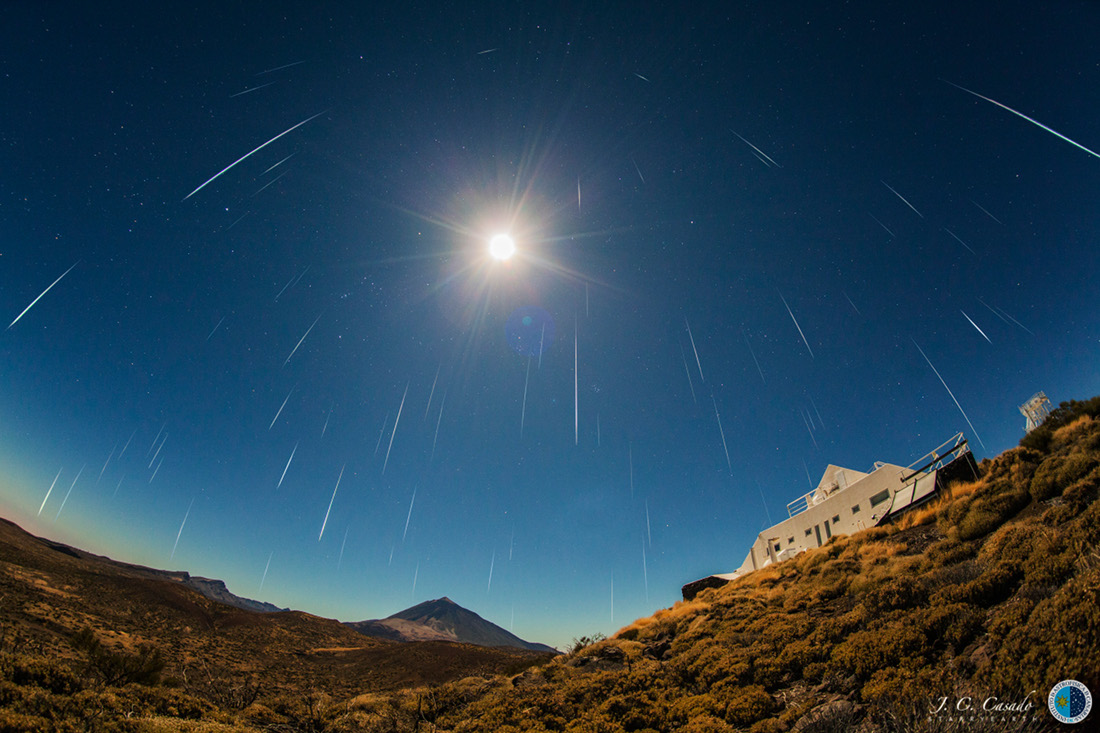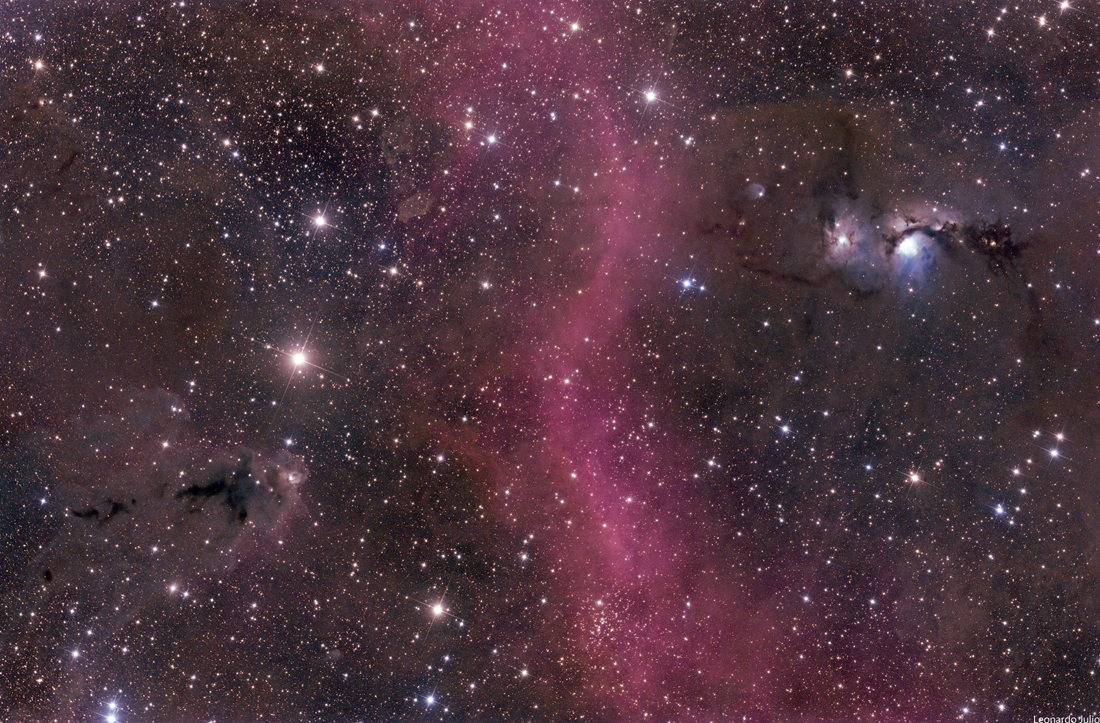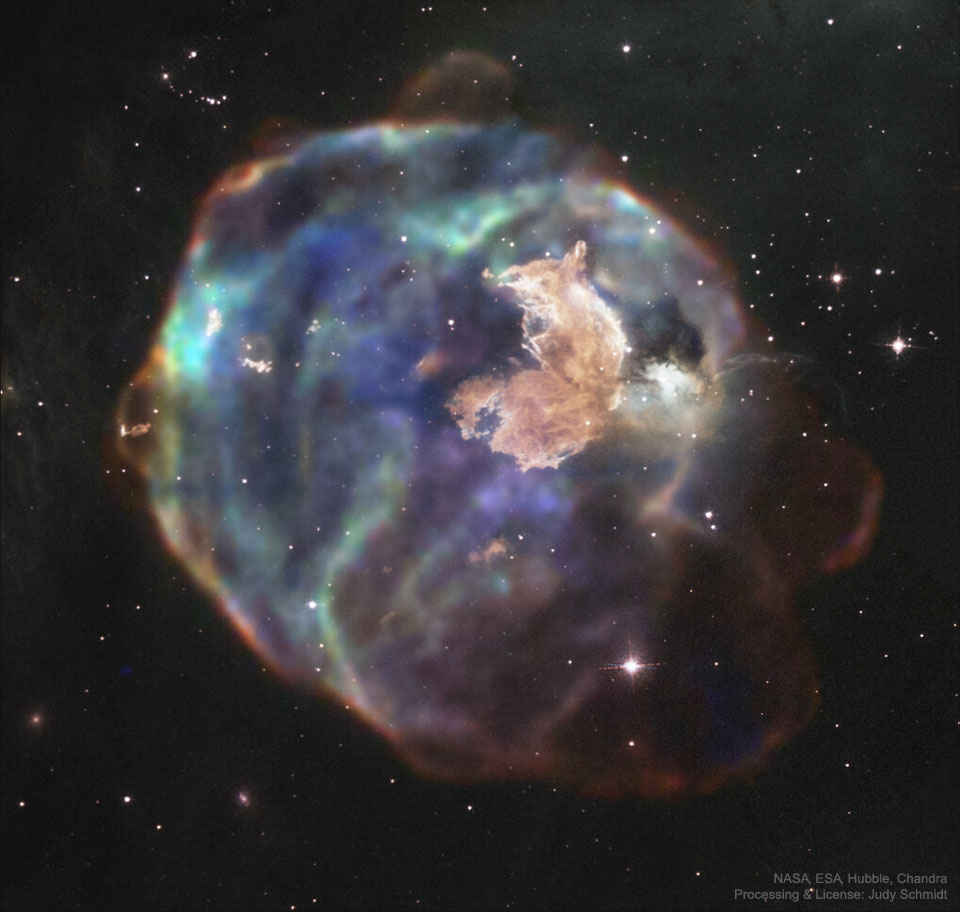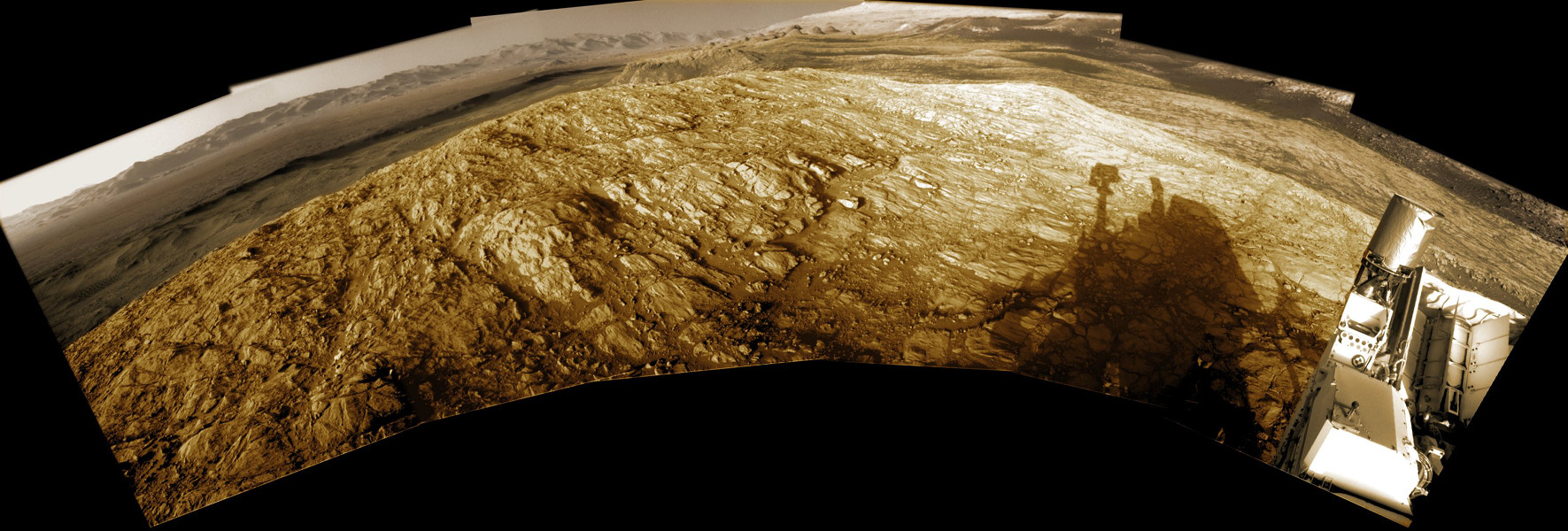
Shadows grow long near sunset in this wide panoramic view from the Curiosity rover on Mars. Made with Curiosity’s navcam, the scene covers about 200 degrees from north through east to south (left to right), stitched together from frames taken by the Mars rover on sol 2616. That’s just Earth date December 16. Curiosity is perched on top of a plateau on Western Butte. The distant northern rim of Gale crater is visible along the left. Near center is Central Butte, already visited by Curiosity. On the right, the shadow of the rover seems to stretch toward the base of Aeolis Mons (Mount Sharp), a future destination. The monochrome navcam frames have been colorized to approximate the colors of the late martian afternoon. via NASA https://ift.tt/2Z8WrvE








