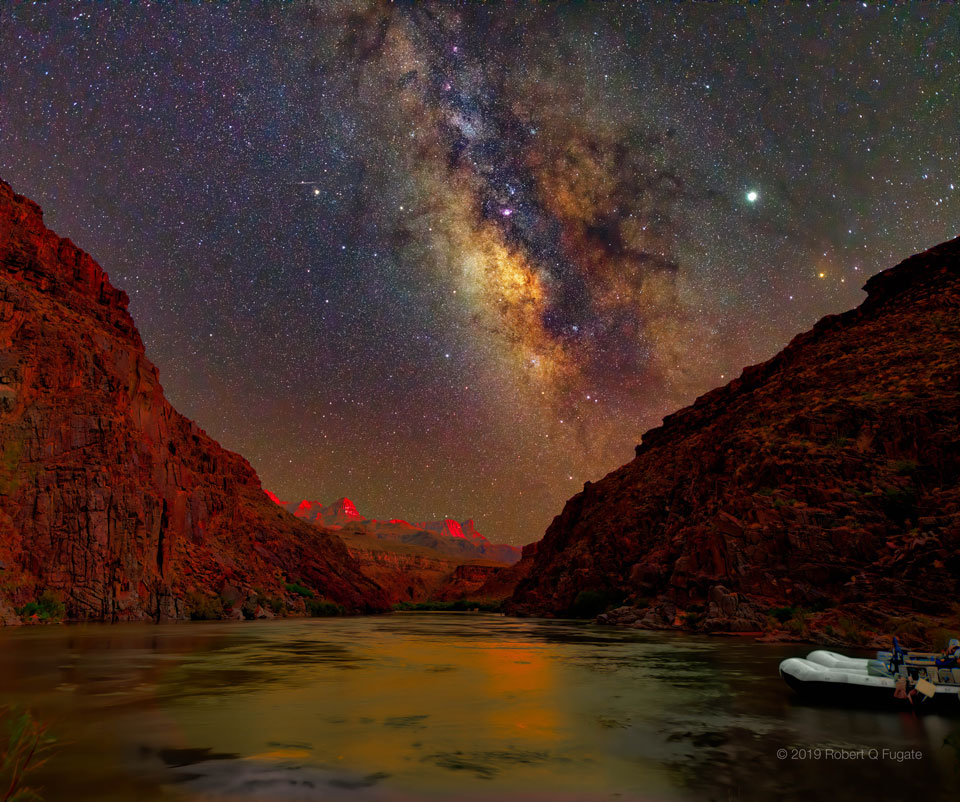
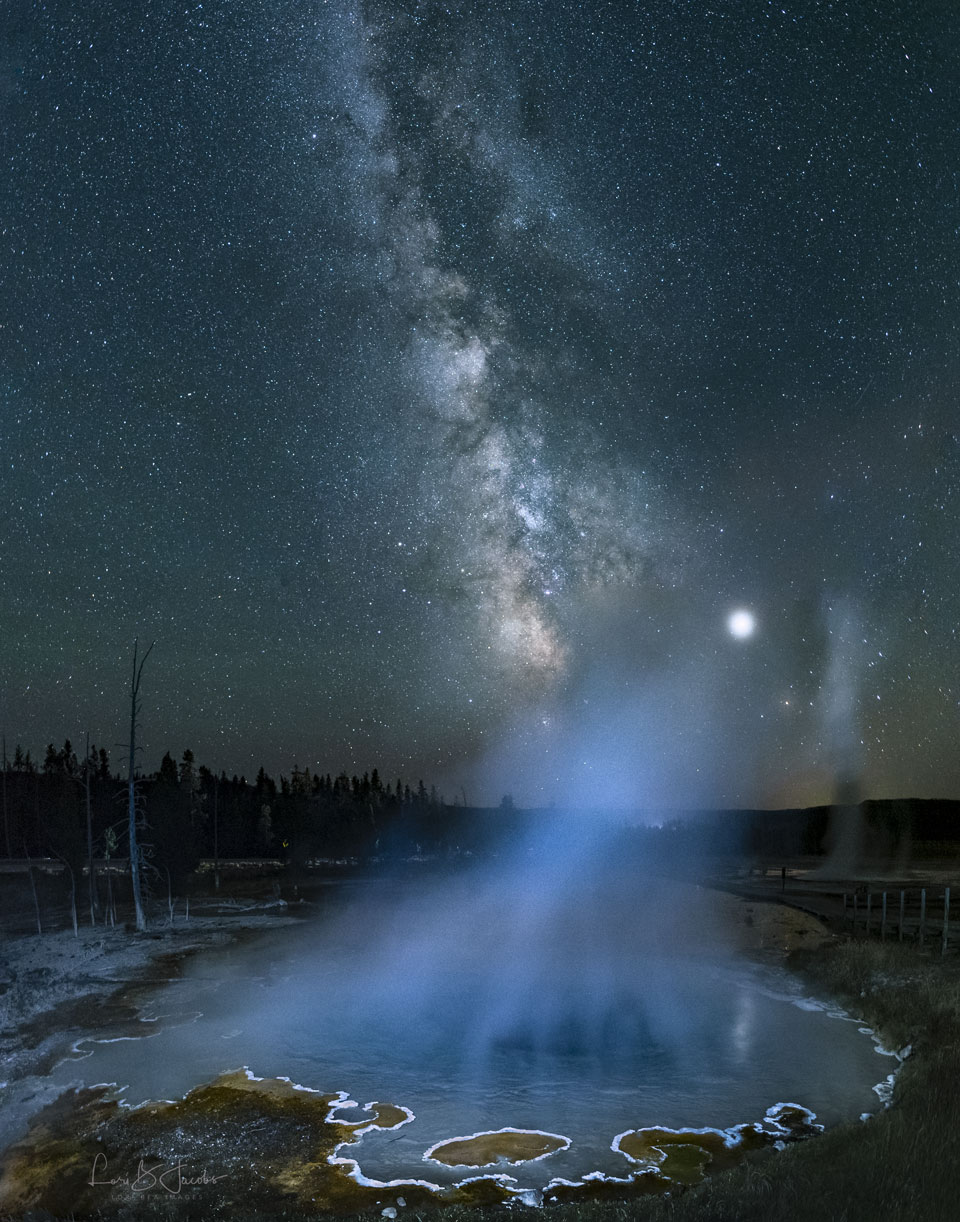
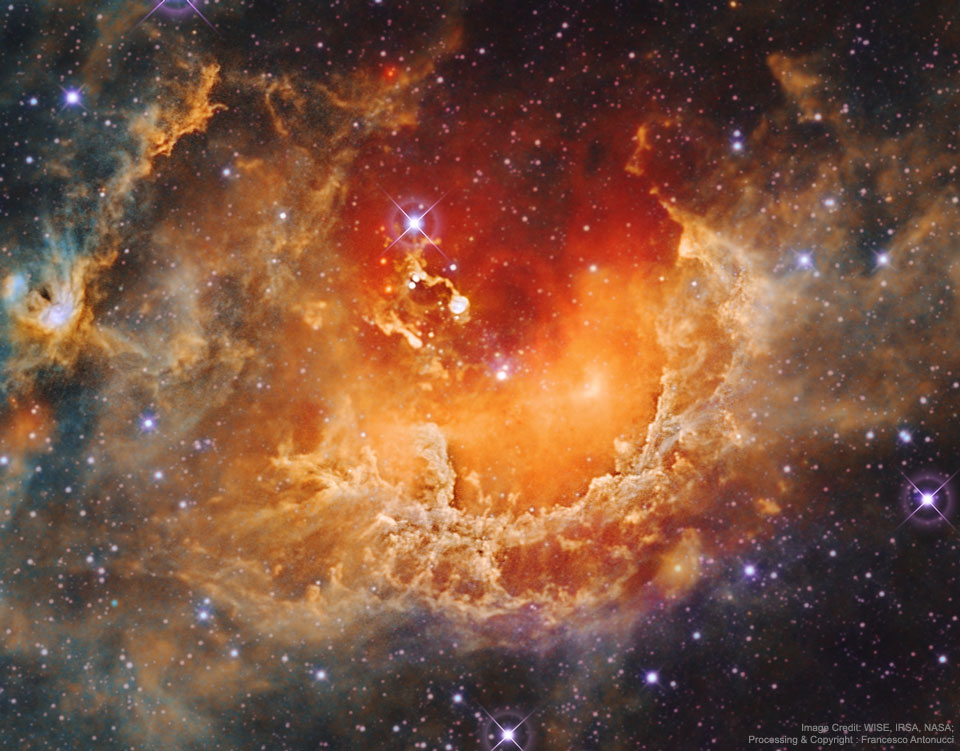
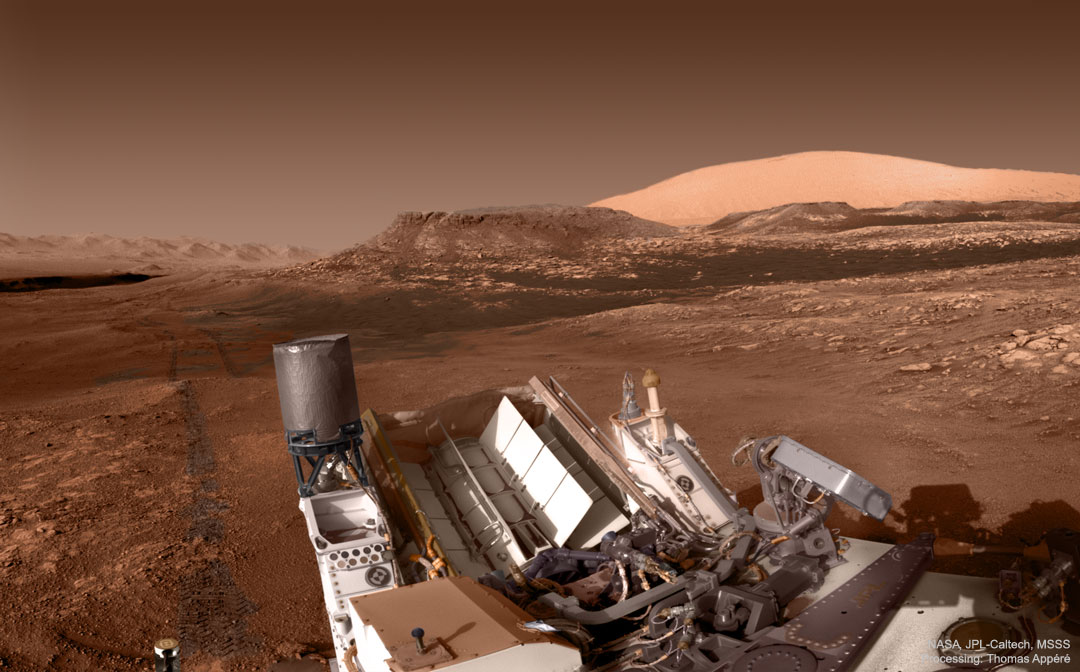
Seeing mountain peaks glow red from inside the Grand Canyon was one of the most incredible sunset experiences of this amateur photographer’s life. They appeared even more incredible later, when digitally combined with an exposure of the night sky — taken by the same camera and from the same location — an hour later. The two images were taken last August from the 220 Mile Canyon campsite on the Colorado River, Colorado, USA. The peaks glow red because they were lit by an usually red sunset. Later, high above, the band of the Milky Way Galaxy angled dramatically down, filled with stars, nebula, and dark clouds of dust. To the Milky Way’s left is the planet Saturn, while to the right is the brighter Jupiter. Although Jupiter and Saturn are now hard to see, Venus will be visible and quite bright to the west in clear skies, just after sunset, for the next two months. via NASA https://ift.tt/2SkztP0