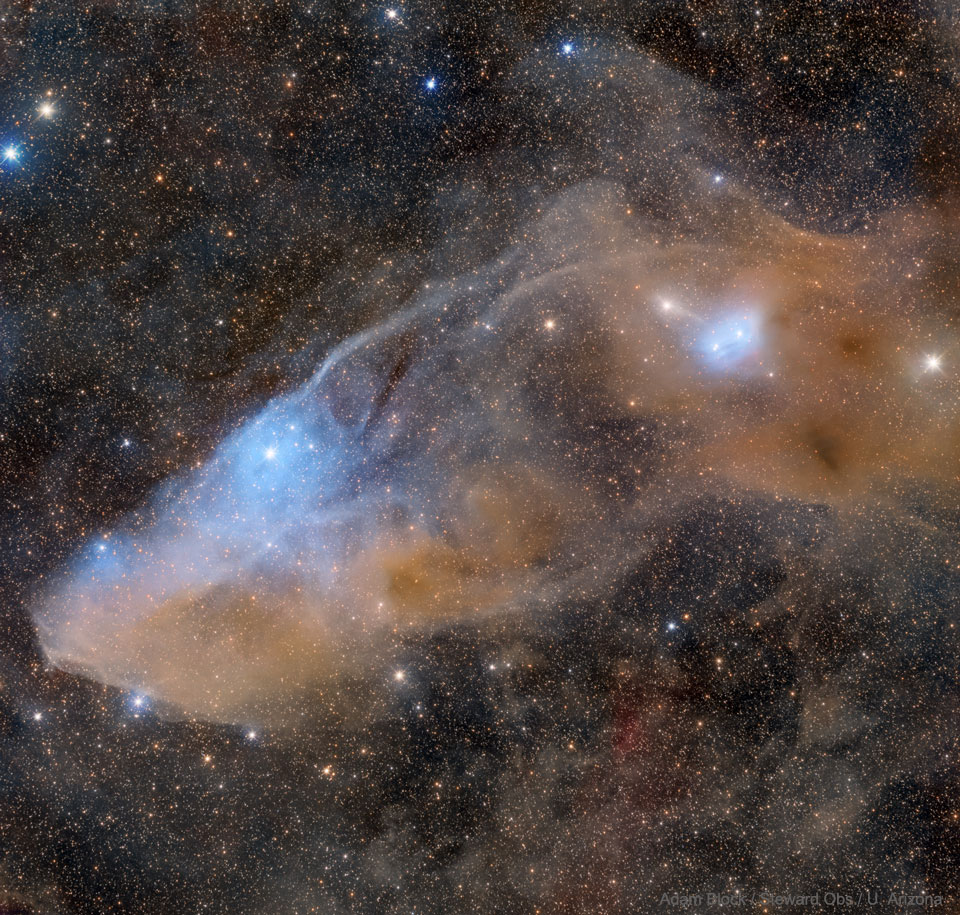
Do you see the horse’s head? What you are seeing is not the famous Horsehead nebula toward Orion but rather a fainter nebula that only takes on a familiar form with deeper imaging. The main part of the here imaged molecular cloud complex is a reflection nebula cataloged as IC 4592. Reflection nebulas are actually made up of very fine dust that normally appears dark but can look quite blue when reflecting the visible light of energetic nearby stars. In this case, the source of much of the reflected light is a star at the eye of the horse. That star is part of Nu Scorpii, one of the brighter star systems toward the constellation of the Scorpion (Scorpius). A second reflection nebula dubbed IC 4601 is visible surrounding two stars to the right of the image center. via NASA https://ift.tt/2TBxVor