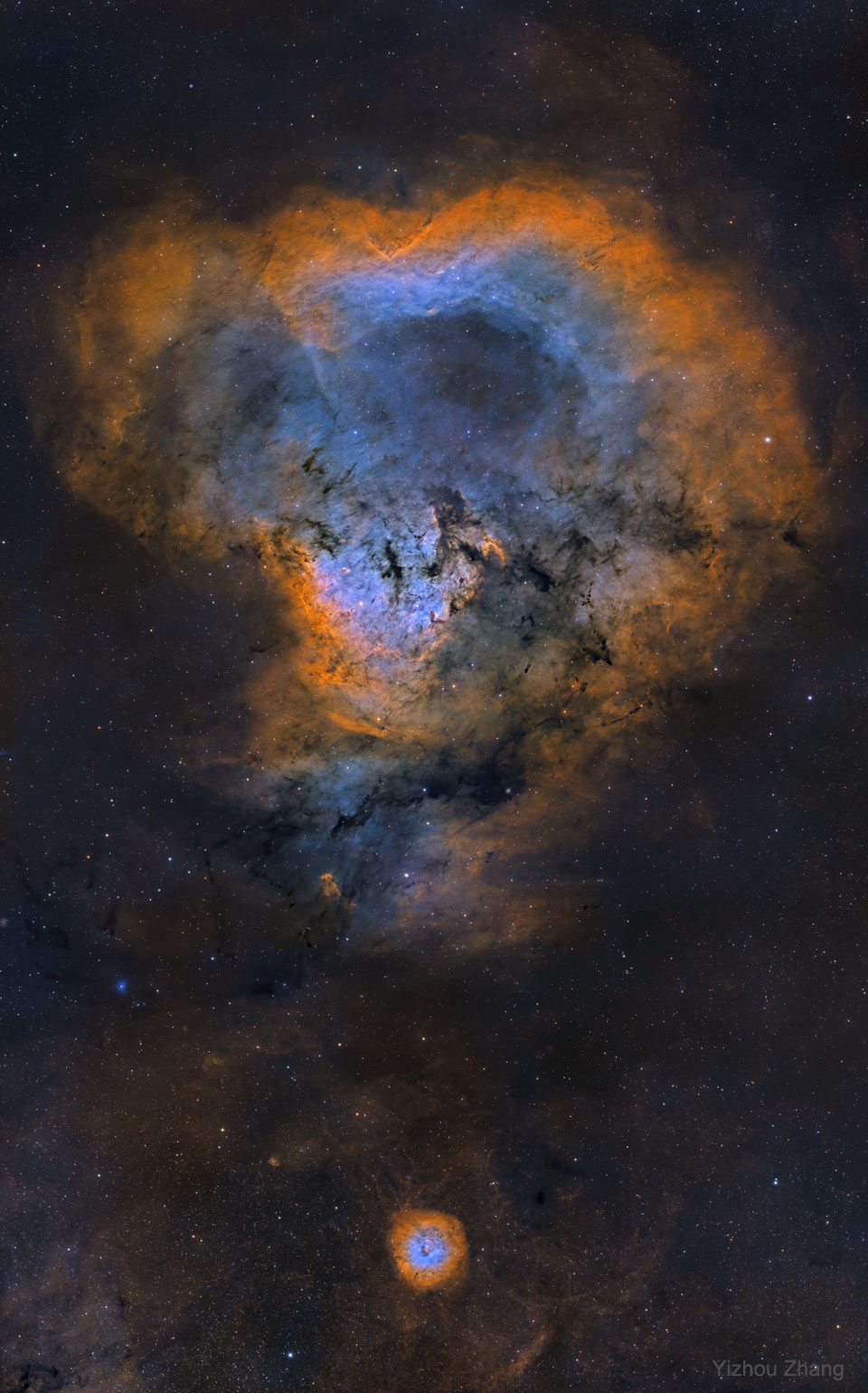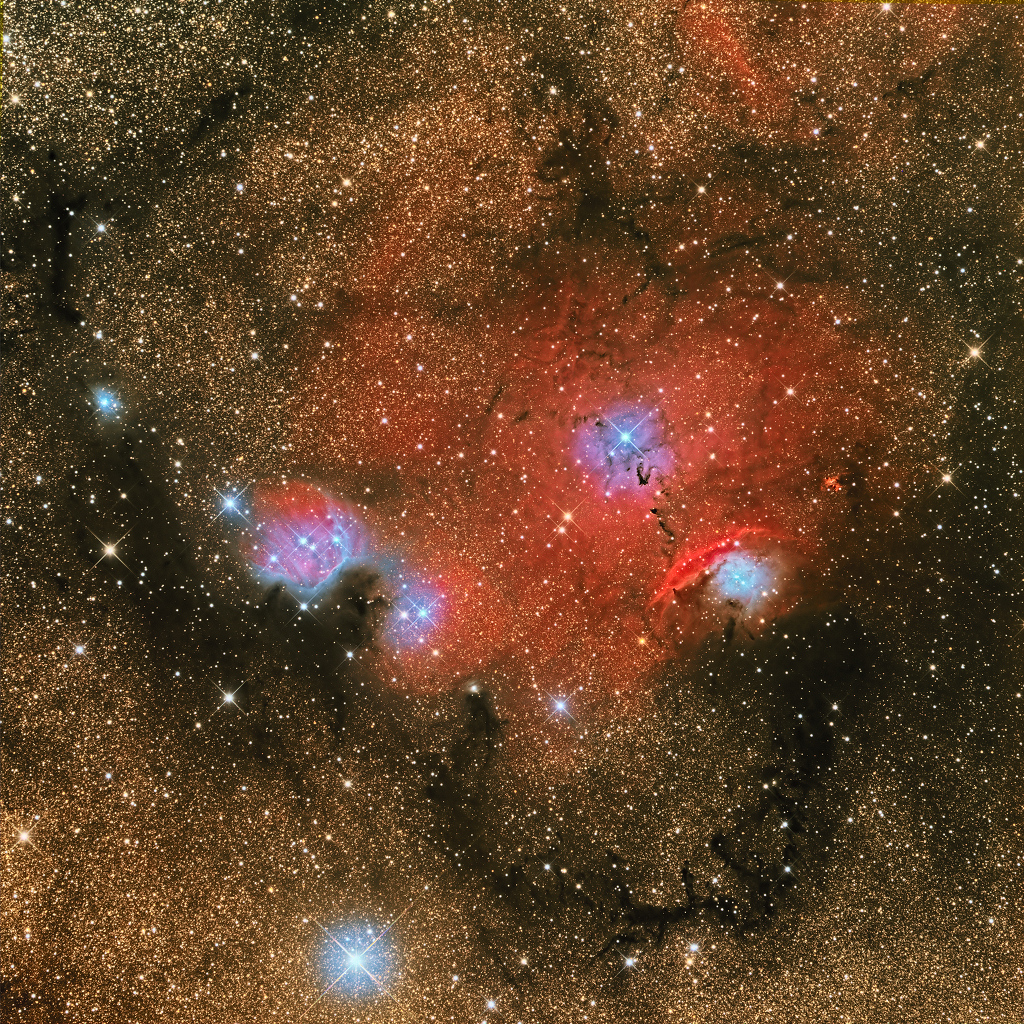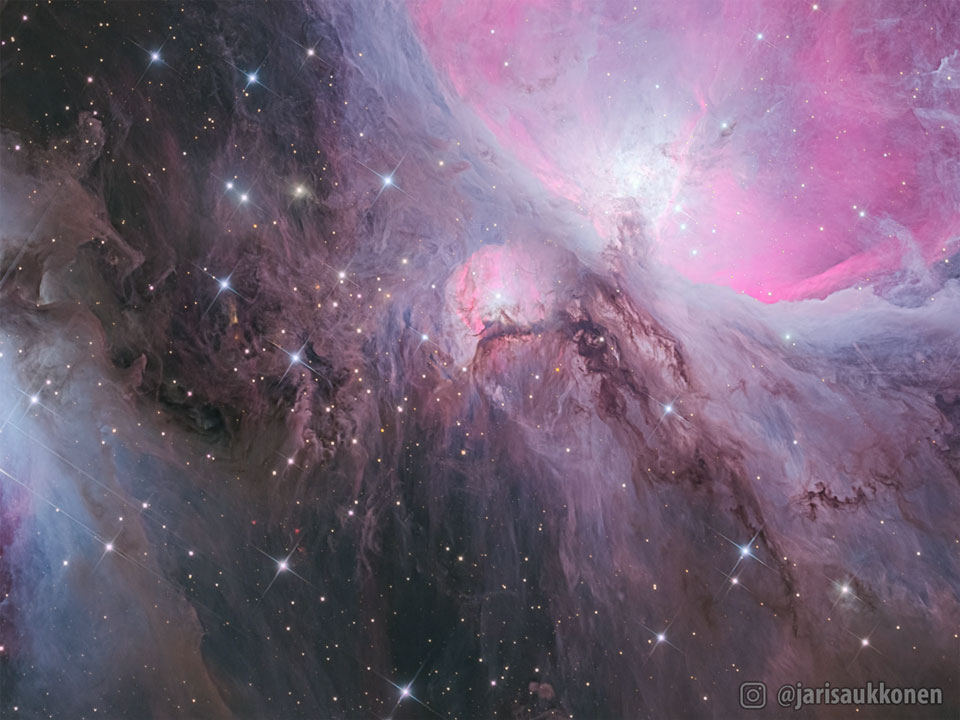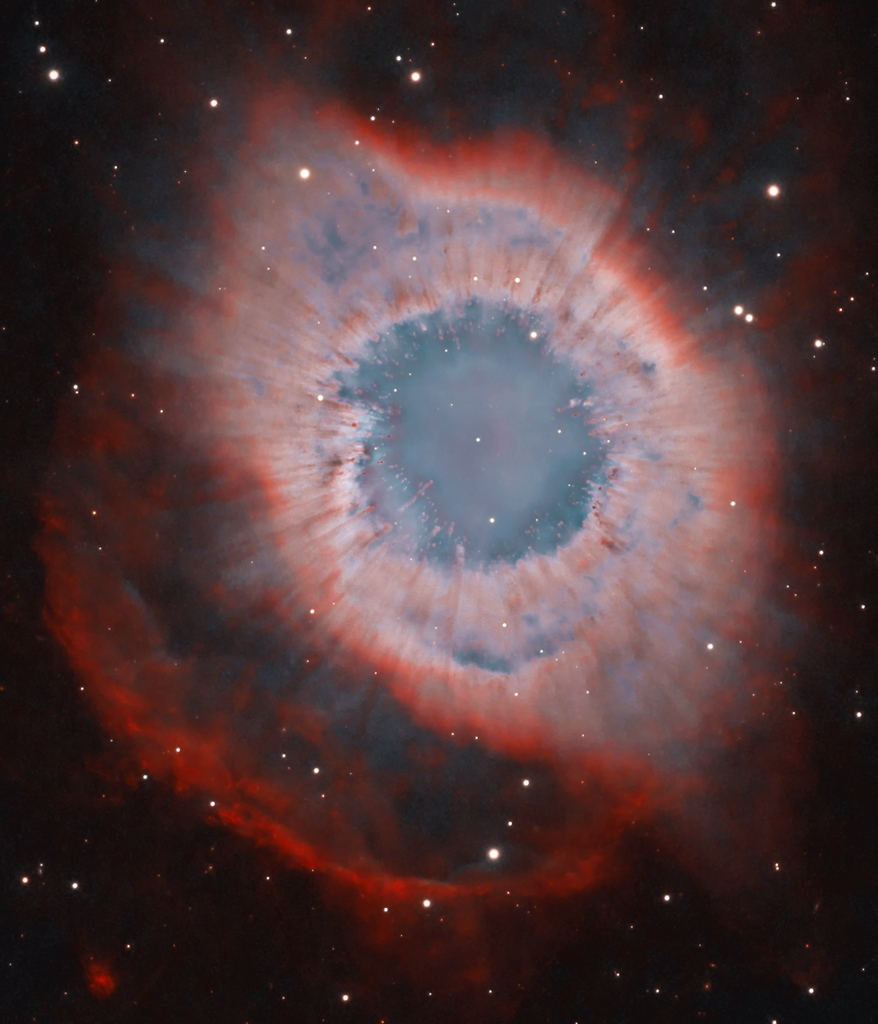
A mere seven hundred light years from Earth, toward the constellation Aquarius, a sun-like star is dying. Its last few thousand years have produced the Helix Nebula (NGC 7293), a well studied and nearby example of a Planetary Nebula, typical of this final phase of stellar evolution. A total of 90 hours of exposure time have gone in to creating this expansive view of the nebula. Combining narrow band image data from emission lines of hydrogen atoms in red and oxygen atoms in blue-green hues, it shows remarkable details of the Helix’s brighter inner region about 3 light-years across. The white dot at the Helix’s center is this Planetary Nebula’s hot, central star. A simple looking nebula at first glance, the Helix is now understood to have a surprisingly complex geometry. via NASA https://ift.tt/3ayz8BN






