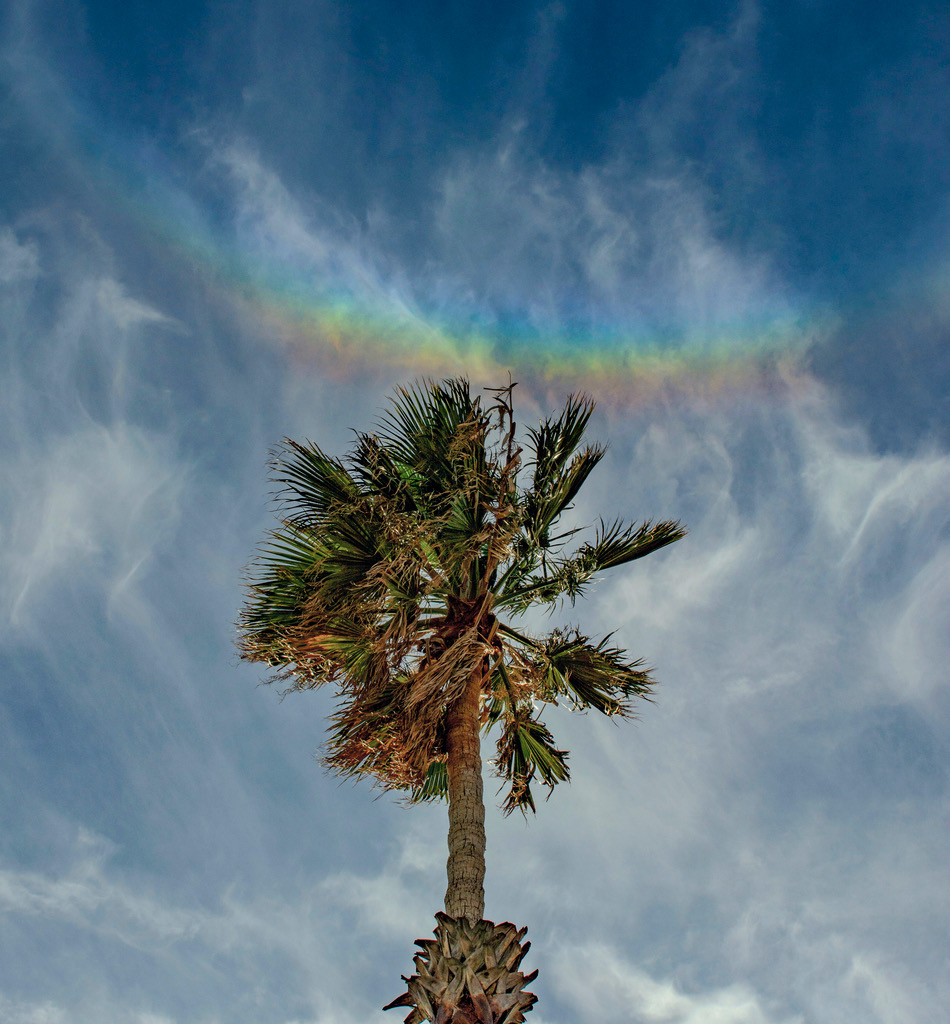
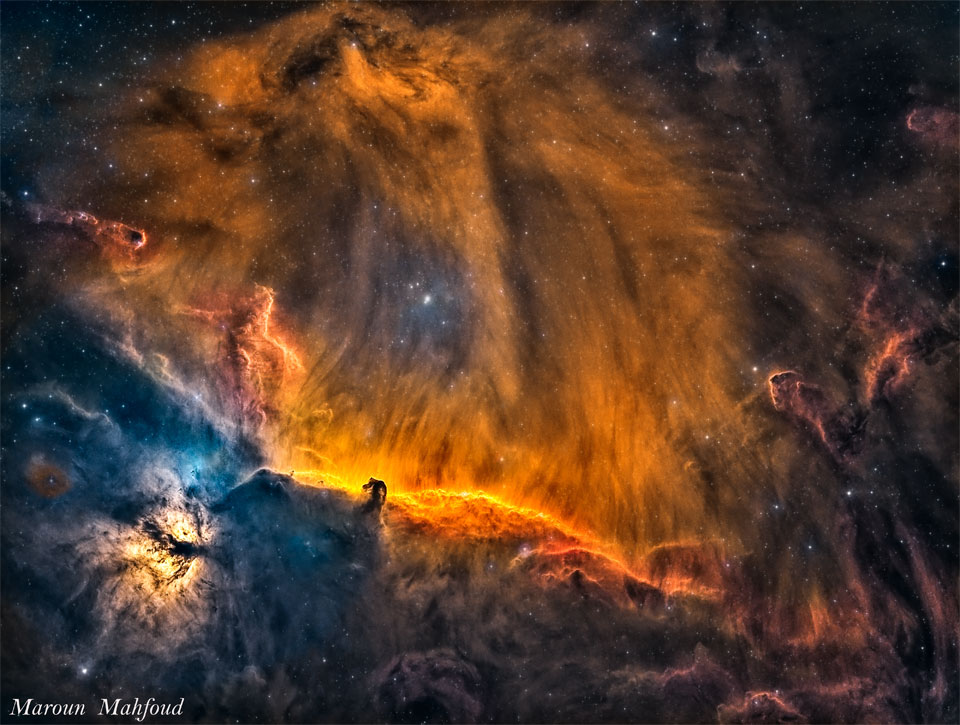
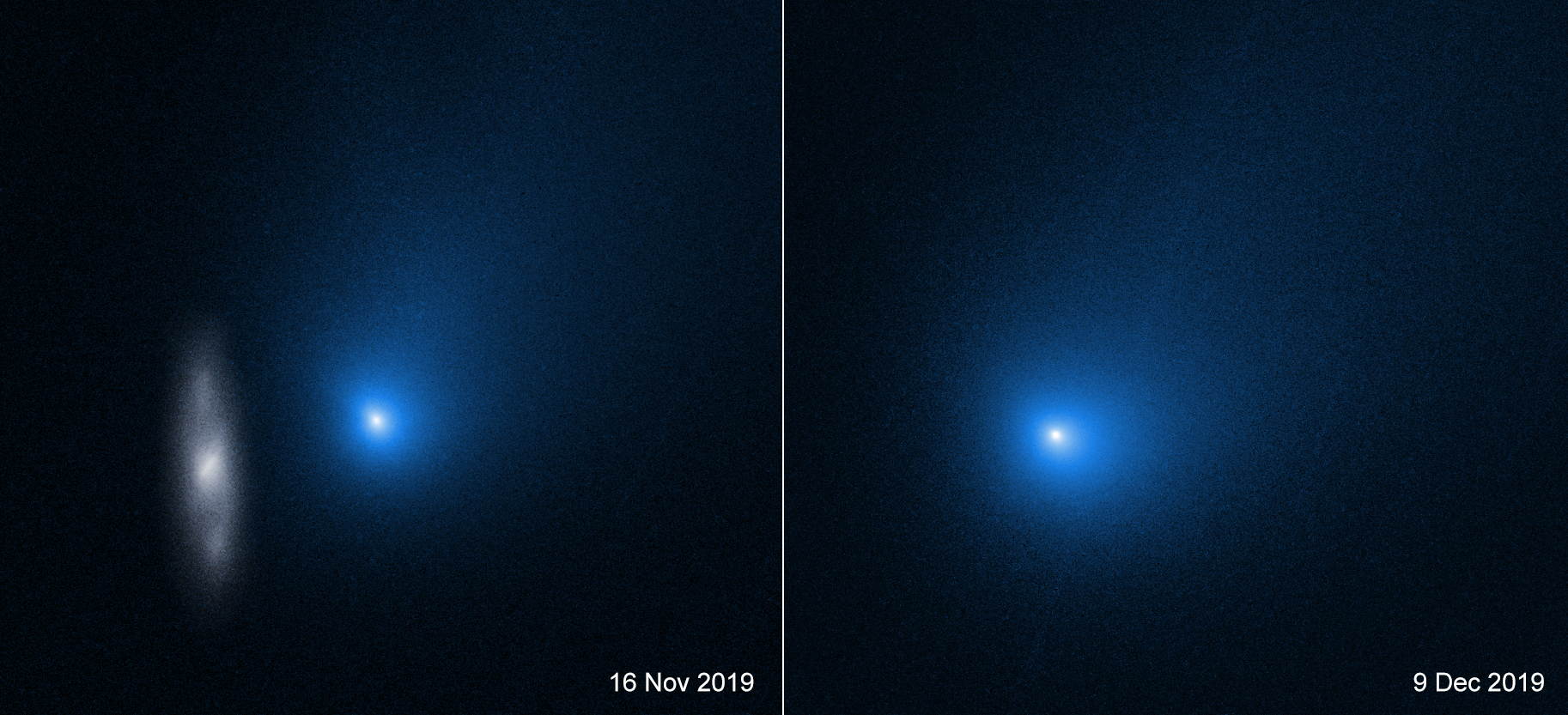
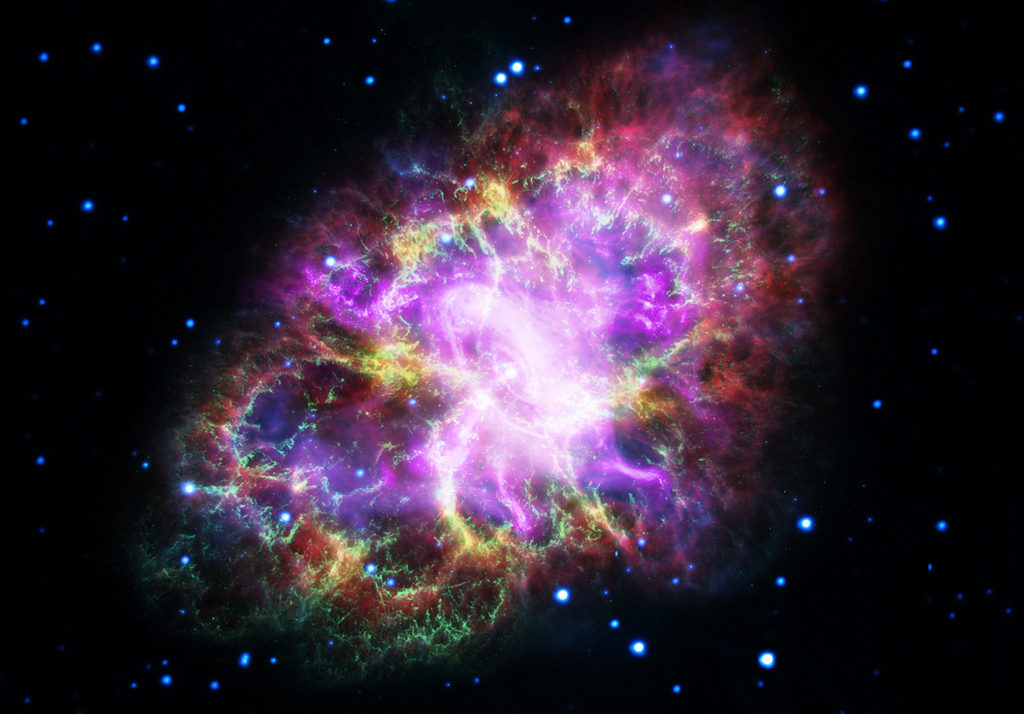
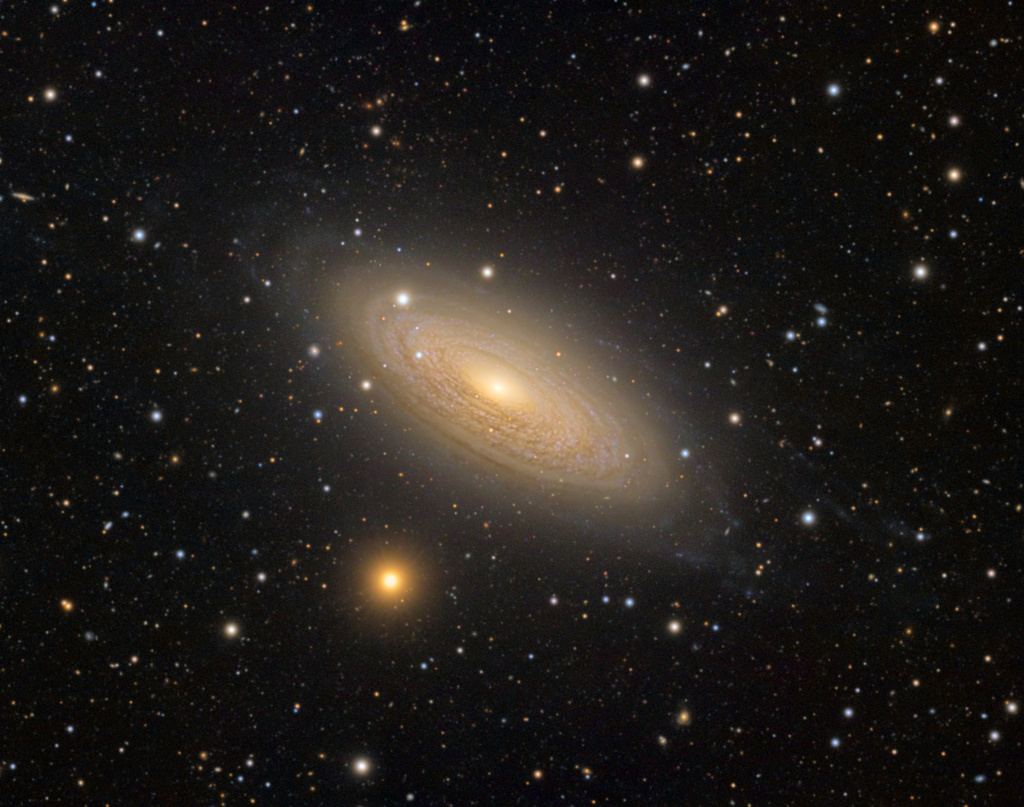
Want to see a rainbow smile? Look near the zenith (straight up) when the sun is low in the sky and you might. This example of an ice halo known as a circumzenithal arc was captured above a palm tree top from Ragusa, Sicily on February 24. The vividly colorful arcs are often called smiling rainbows because of their upside down curvature and colors. For circumzenithal arcs the zenith is at the center and red is on the outside, compared to rainbows whose arcs bend toward the horizon after a downpour. True rainbows are formed by water droplets refracting the sunlight to produce a spectrum of colors, though. Circumzenithal arcs are the product of refraction and reflection in flat hexagonal ice crystals, like the ice crystals that create sundogs, formed in high thin clouds. via NASA https://ift.tt/ubIESMO