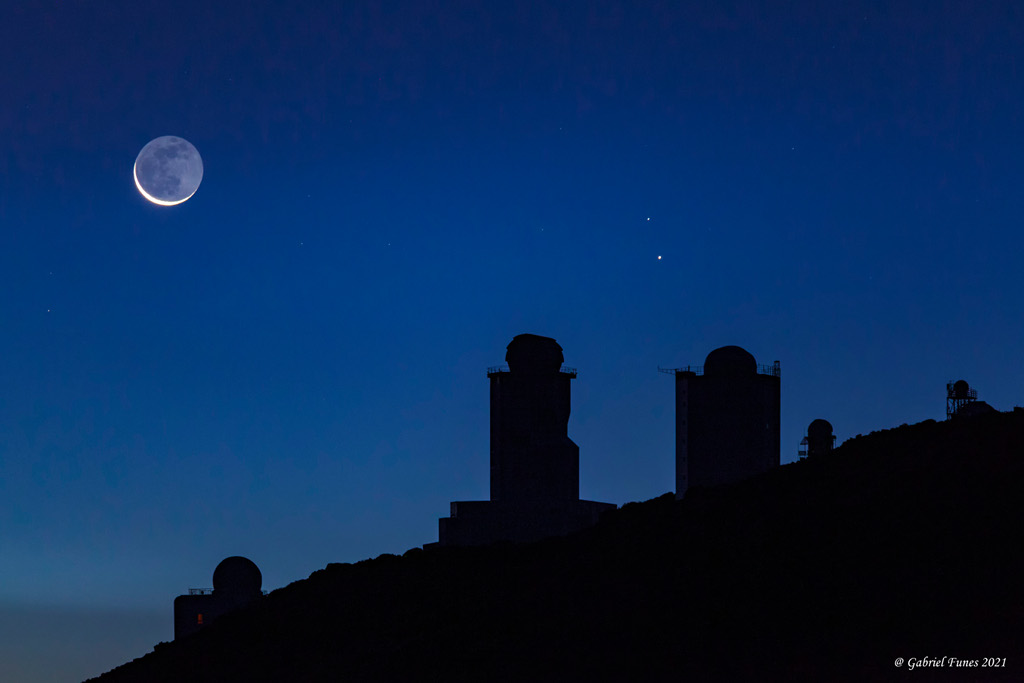
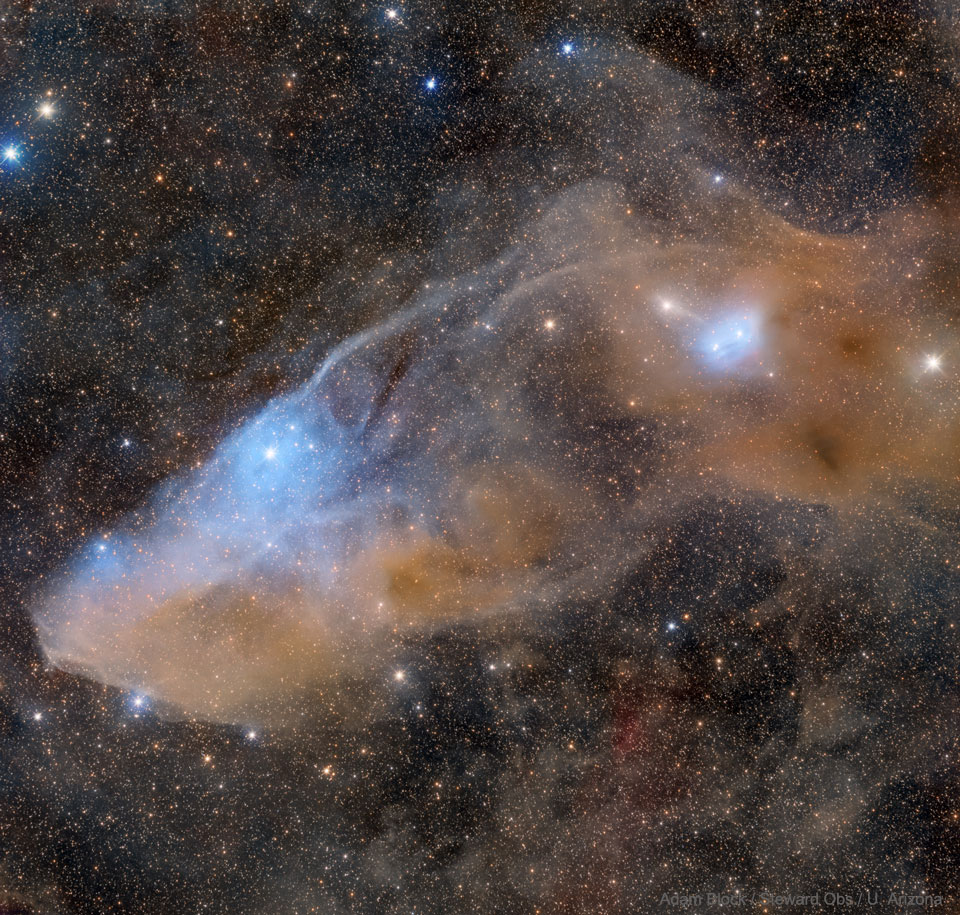
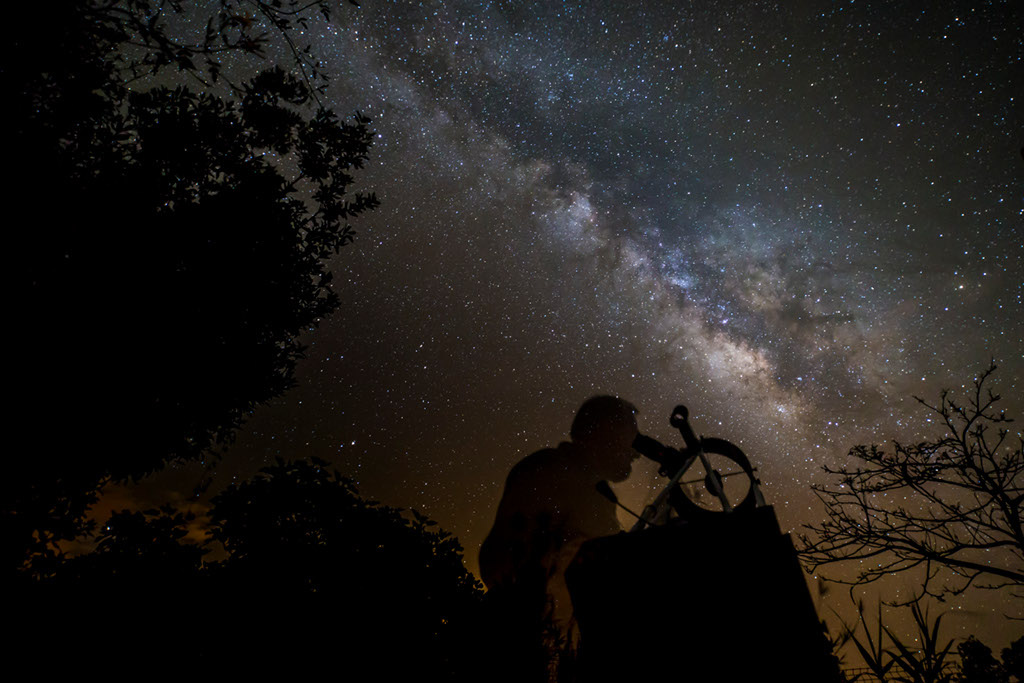
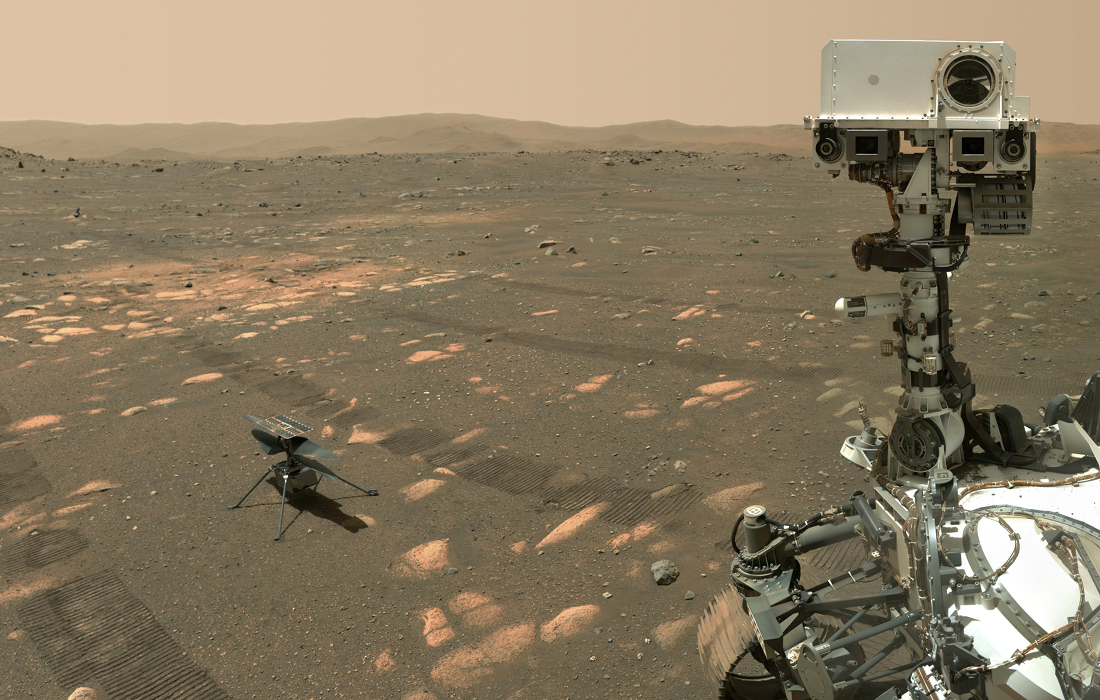
On July 8th early morning risers saw Mercury near an old Moon low on the eastern horizon. On that date bright planet, faint glow of lunar night side, and sunlit crescent were captured in this predawn skyscape from Tenerife’s Teide National Park in the Canary Islands. Never far from the Sun in planet Earth’s sky, the fleeting inner planet shines near its brightest in the morning twilight scene. Mercury lies just below the zeta star of the constellation Taurus, Zeta Tauri, near the tip of the celestial bull’s horn. Of course the Moon’s ashen glow is earthshine, earthlight reflected from the Moon’s night side. A description of earthshine, in terms of sunlight reflected by Earth’s oceans illuminating the Moon’s dark surface, was written over 500 years ago by Leonardo da Vinci. Waiting for the coming dawn in the foreground are the Teide Observatory’s sentinels of the Sun, also known as (large domes left to right) the THEMIS, VTT, and GREGOR solar telescopes. via NASA https://ift.tt/3AQHHnt