How does your favorite planet spin? Does it spin rapidly around a nearly vertical axis, or horizontally, or backwards? The featured video animates NASA images of all eight planets in our Solar System to show them spinning side-by-side for an easy comparison. In the time-lapse video, a day on Earth — one Earth rotation — takes just a few seconds. Jupiter rotates the fastest, while Venus spins not only the slowest (can you see it?), but backwards. The inner rocky planets, across the top, most certainly underwent dramatic spin-altering collisions during the early days of the Solar System. The reasons why planets spin and tilt as they do remains a topic of research with much insight gained from modern computer modeling and the recent discovery and analysis of hundreds of exoplanets: planets orbiting other stars. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/30uLuEZ
Archives mensuelles : mai 2019
Atlas, Daphnis, and Pan
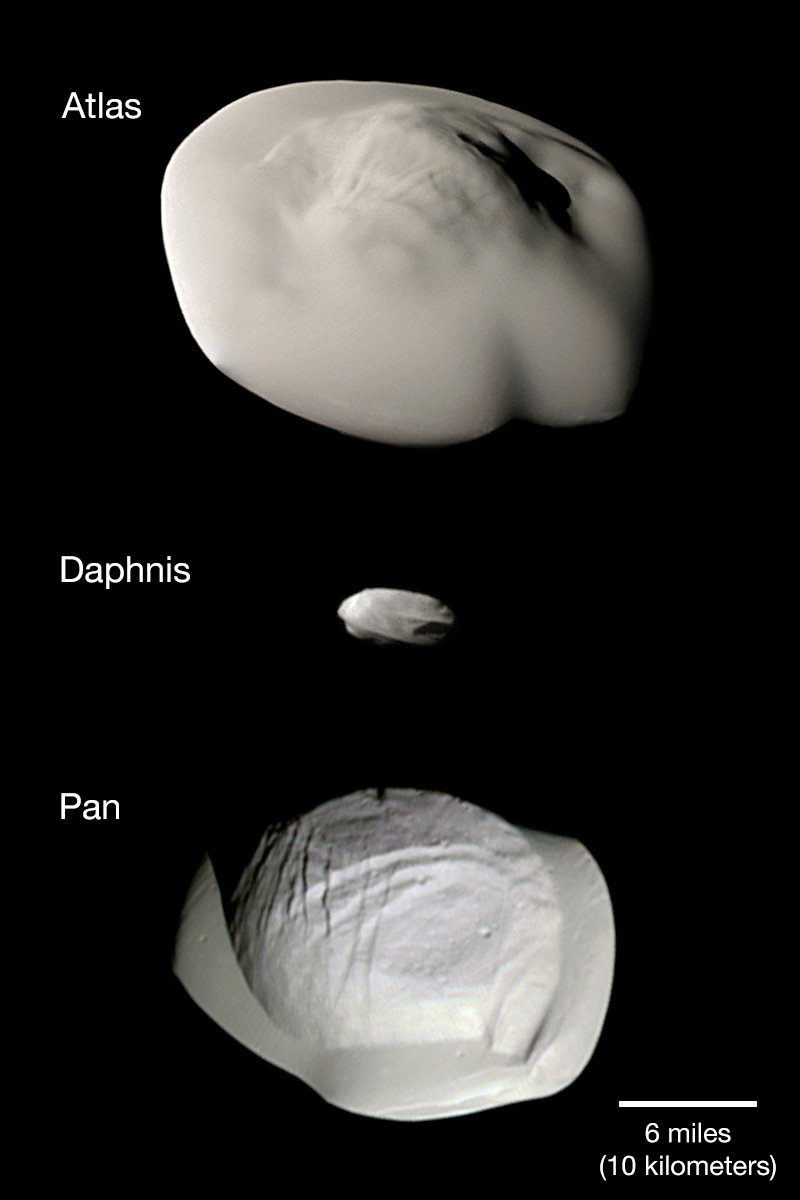
Atlas, Daphnis, and Pan are small, inner, ring moons of Saturn. They are shown at the same scale in this montage of images by the Cassini spacecraft that made its grand final orbit of the ringed planet in September 2017. In fact, Daphnis was discovered in Cassini images from 2005. Atlas and Pan were first sighted in images from the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. Flying saucer-shaped Atlas orbits near the outer edge of Saturn’s bright A Ring while Daphnis orbits inside the A Ring’s narrow Keeler Gap and Pan within the A Ring’s larger Encke Gap. The curious equatorial ridges of the small ring moons could be built up by the accumulation of ring material over time. Even diminutive Daphnis makes waves in the ring material as it glides along the edge of the Keeler Gap. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2JqRWHK
Ma journée en garde à vue.
RS Puppis
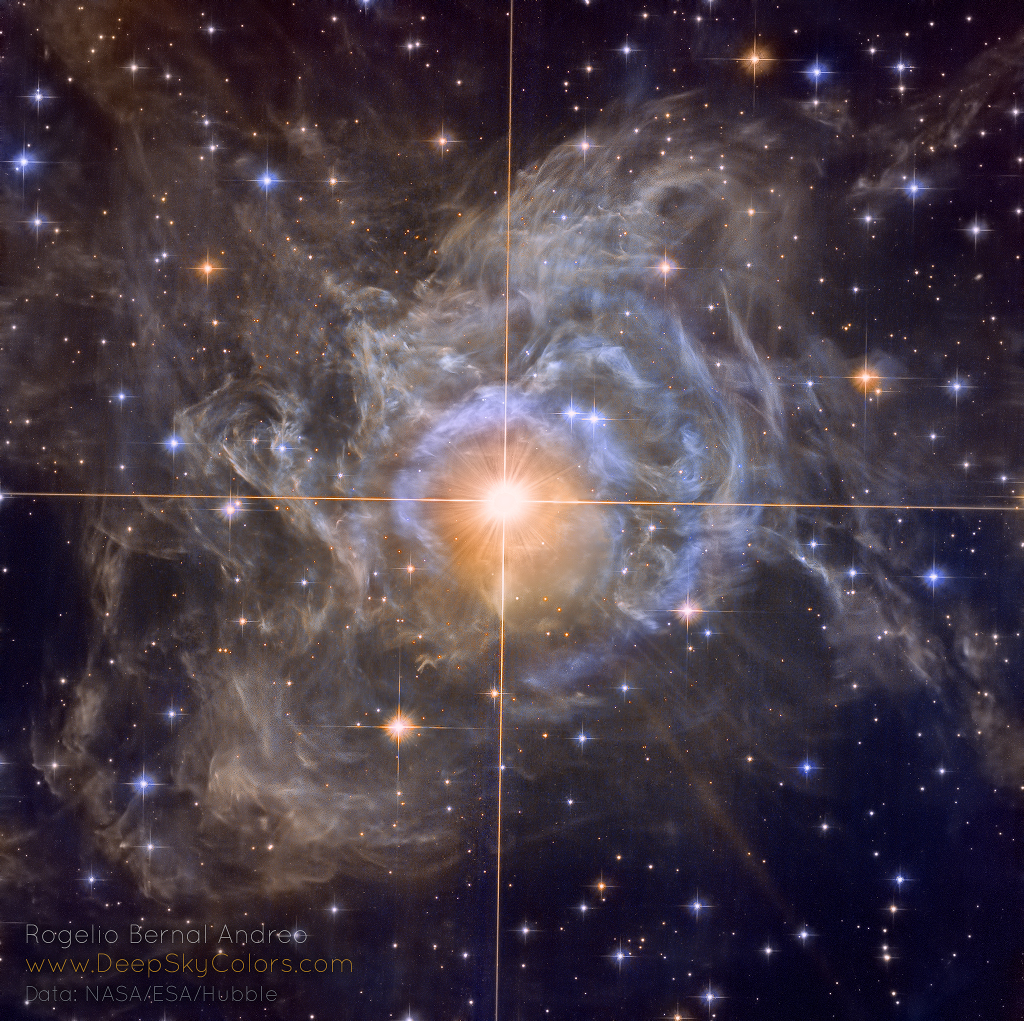

Pulsating RS Puppis, the brightest star in the image center, is some ten times more massive than our Sun and on average 15,000 times more luminous. In fact, RS Pup is a Cepheid variable star, a class of stars whose brightness is used to estimate distances to nearby galaxies as one of the first steps in establishing the cosmic distance scale. As RS Pup pulsates over a period of about 40 days, its regular changes in brightness are also seen along its surrounding nebula delayed in time, effectively a light echo. Using measurements of the time delay and angular size of the nebula, the known speed of light allows astronomers to geometrically determine the distance to RS Pup to be 6,500 light-years, with a remarkably small error of plus or minus 90 light-years. An impressive achievement for stellar astronomy, the echo-measured distance also more accurately establishes the true brightness of RS Pup, and by extension other Cepheid stars, improving the knowledge of distances to galaxies beyond the Milky Way. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2VGw7us
Dark Skies: Turn on the Night
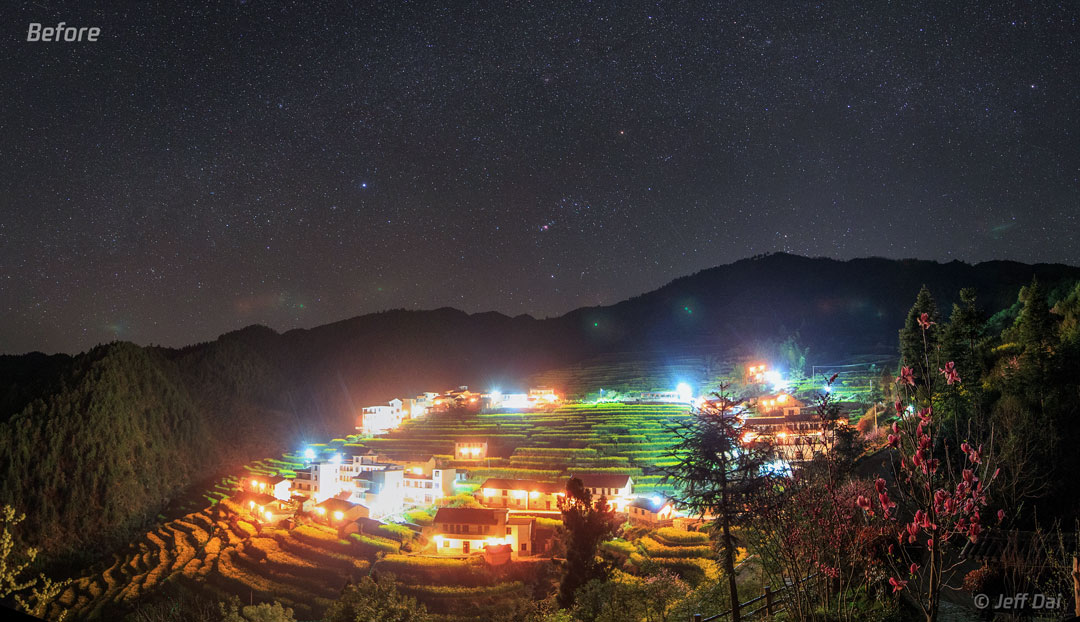

Have you ever experienced a really dark night sky? One common and amazing feature is the glowing band of our Milky Way galaxy stretching from horizon to horizon. If you live in or near a big city, though, you might not know this because city lights reflecting off the Earth’s atmosphere could only allow you to see the Moon and a few stars. Today, however, being UNESCO’s International Day of Light, the International Astronomical Union is asking people to Turn on the Night by trying to better understand, and in the future better reduce, light pollution. You can practice even now by going to the main APOD website at NASA and hovering your cursor over the Before image. The After picture that comes up is a panorama of four exposures taken with the same camera and from the same location, showing what happened recently in China when people in Kaihua County decided to turn down many of their lights. Visible in the Before picture are the stars Sirius (left of center) and Betelgeuse, while visible in the After picture are thousands of stars with the arching band of our Milky Way Galaxy. Humanity has lived for millennia under a dark night sky, and connecting to it has importance for both natural and cultural heritage. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2WP64hc
Anemic Spiral NGC 4921 from Hubble
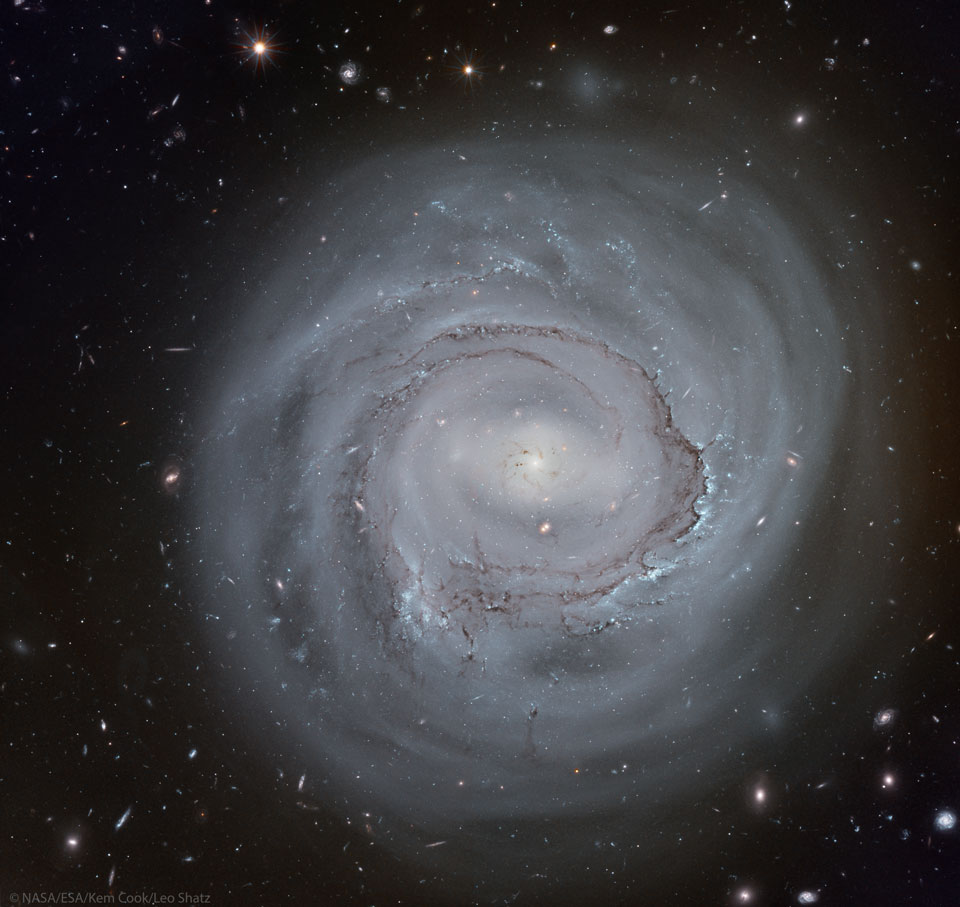

How far away is spiral galaxy NGC 4921? It’s surpringly important to know. Although presently estimated to be about 300 million light years distant, a more precise determination could be coupled with its known recession speed to help humanity better calibrate the expansion rate of the entire visible universe. Toward this goal, several images were taken by the Hubble Space Telescope in order to help identify key stellar distance markers known as Cepheid variable stars. Since NGC 4921 is a member of the Coma Cluster of Galaxies, refining its distance would also allow a better distance determination to one of the largest nearby clusters in the local universe. The magnificent spiral NGC 4921 has been informally dubbed anemic because of its low rate of star formation and low surface brightness. Visible in the featured image are, from the center, a bright nucleus, a bright central bar, a prominent ring of dark dust, blue clusters of recently formed stars, several smaller companion galaxies, unrelated galaxies in the far distant universe, and unrelated stars in our Milky Way Galaxy. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2WDF8Rj
Rho Ophiuchi Wide Field
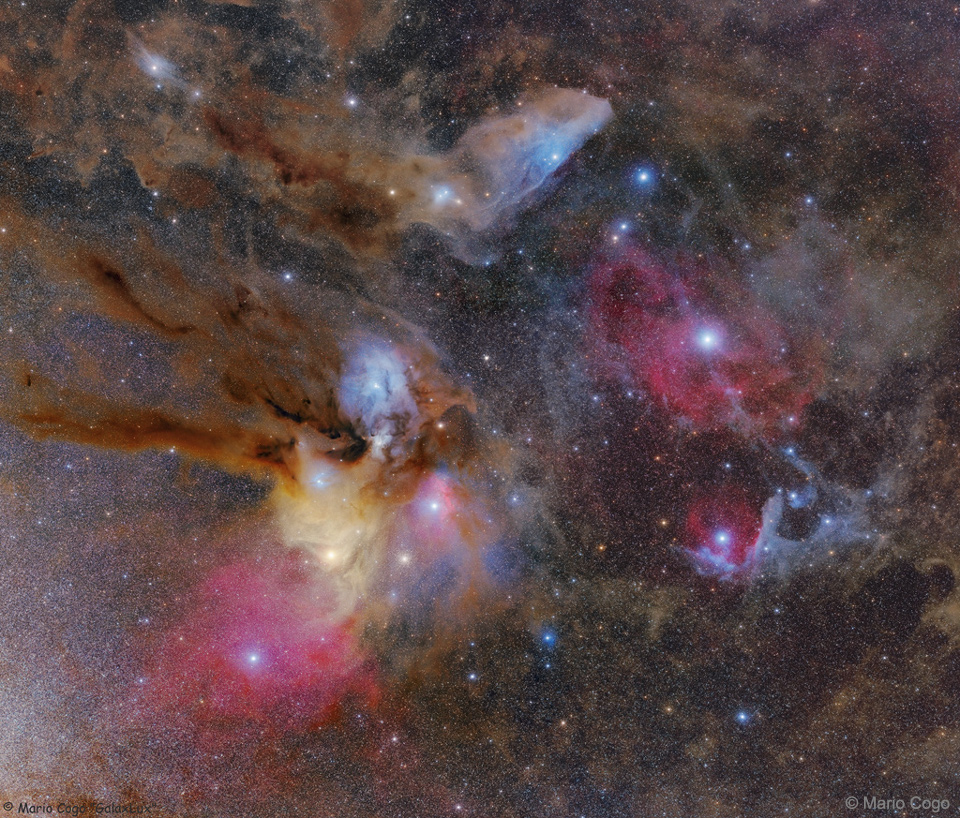

The colorful clouds surrounding the star system Rho Ophiuchi compose one of the closest star forming regions. Rho Ophiuchi itself is a binary star system visible in the blue reflection nebula just to the left of the image center. The star system, located only 400 light years away, is distinguished by its multi-colored surroundings, which include a red emission nebula and numerous light and dark brown dust lanes. Near the lower left of the Rho Ophiuchi molecular cloud system is the yellow star Antares, while a distant but coincidently-superposed globular cluster of stars, M4, is visible just to the right of Antares. Near the image top lies IC 4592, the Blue Horsehead nebula. The blue glow that surrounds the Blue Horsehead’s eye — and other stars around the image — is a reflection nebula composed of fine dust. On the featured image right is a geometrically angled reflection nebula cataloged as Sharpless 1. Here, the bright star near the dust vortex creates the light of surrounding reflection nebula. Although most of these features are visible through a small telescope pointed toward the constellations of Ophiuchus, Scorpius, and Sagittarius, the only way to see the intricate details of the dust swirls, as featured above, is to use a long exposure camera. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2Yim6jU
Milky Way, Launch, and Landing
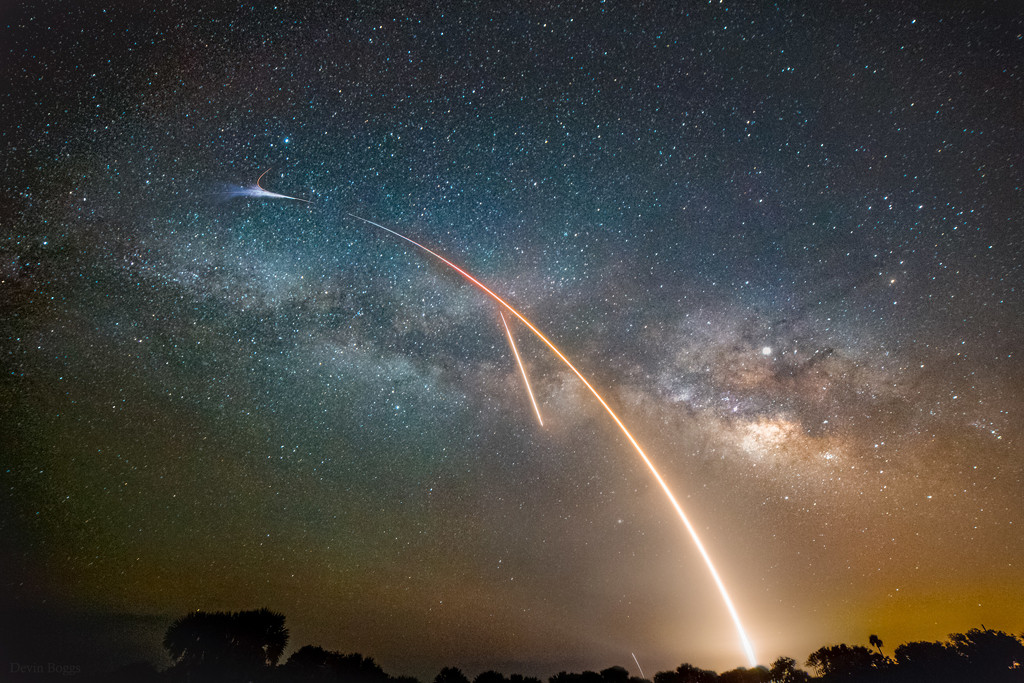

The Milky Way doesn’t look quite this colorful and bright to the eye, but a rocket launch does. So a separate deep exposure with a sensitive digital camera was used in this composite skyscape to bring out our galaxy’s central crowded starfields and cosmic dust clouds. In the scene from Merritt Island National Wildlife Refuge, a nine minute long exposure begun about 20 minutes after the Miky Way image recorded a rocket launch and landing. The Falcon 9 rocket, named for the Millennium Falcon of Star Wars fame, appropriately launched a Dragon resupply ship to the International Space Station in the early morning hours of May the 4th. The plume and flare at the peak of the launch arc mark the rocket’s first stage boost back burn. Two shorter diagonal streaks are the rocket engines bringing the Falcon 9 stage back to an offshore landing on autonomous drone ship Of course I Still Love You. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2vQMwgz
Halley Dust and Milky Way
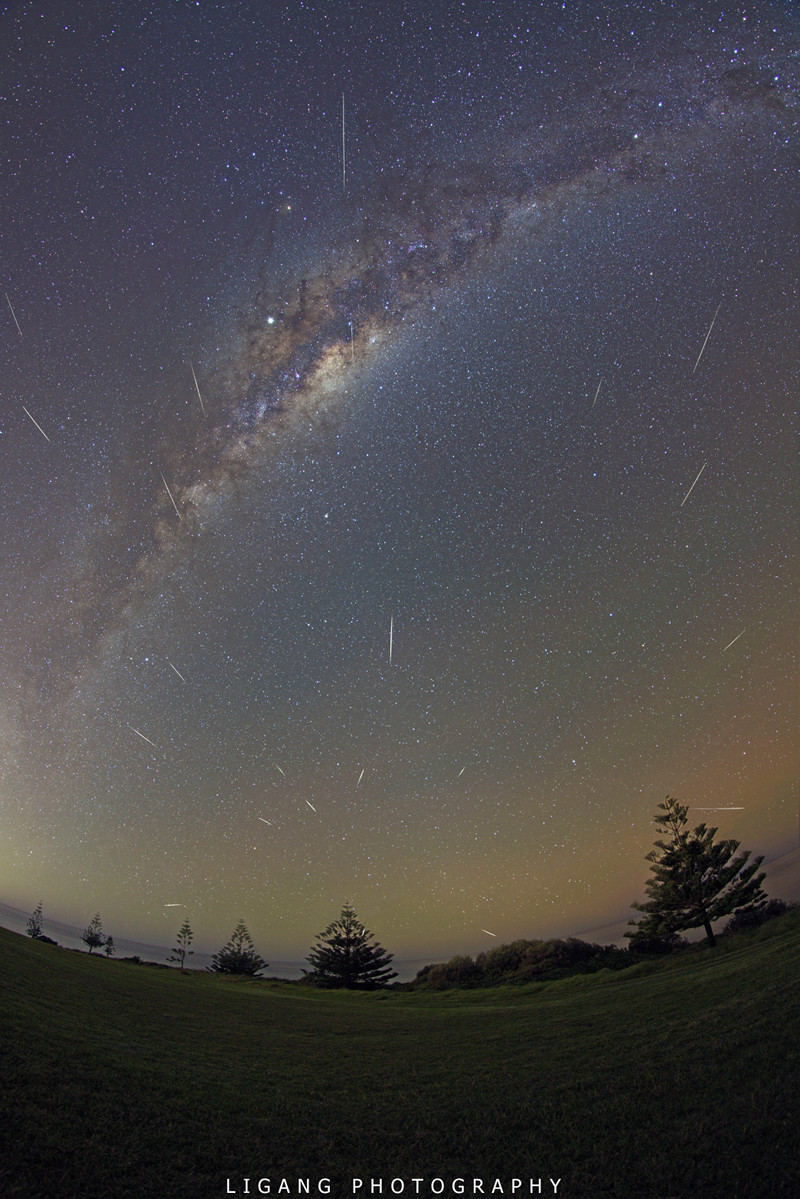

Grains of cosmic dust streaked through the mostly moonless night skies of May 7. Swept up as planet Earth plowed through the debris streams left behind by periodic Comet Halley, the annual meteor shower is known as the Eta Aquarids. Though it was made about a day after the shower’s predicted maximum, this composite image still captures 20 meteors in exposures taken over a 2 hour period, registered on a background exposure of the sky. The meteor trails point back to the shower radiant near eponymous faint star Eta Aquarii close to the horizon, seen from 100 kilometers south of Sydney Australia. Known for speed, Eta Aquarid meteors move fast, entering the atmosphere at about 66 kilometers per second. Brilliant Jupiter shines near the central bulge of the Milky Way high above the horizon. The Southern Cross is just tucked in to the upper right corner of the frame. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2YoPe9f
The Great Nebula in Carina
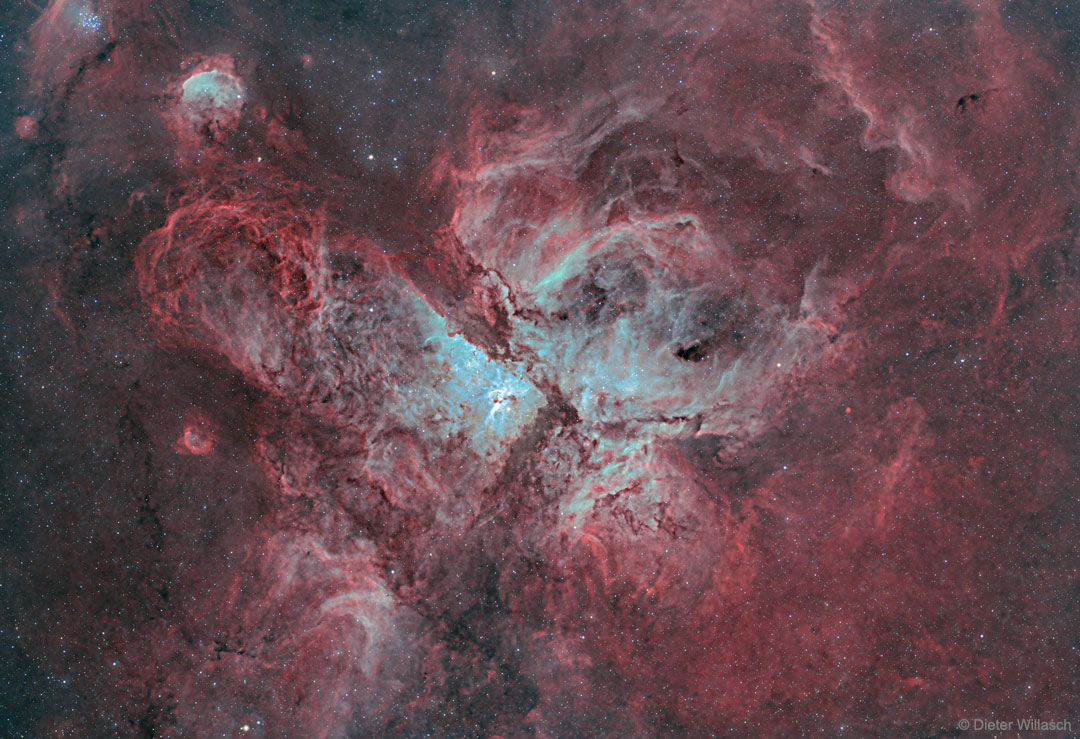

What’s happening in the center of the Carina Nebula? Stars are forming, dying, and leaving an impressive tapestry of dark dusty filaments. The entire Carina Nebula, cataloged as NGC 3372, spans over 300 light years and lies about 8,500 light-years away in the constellation of Carina. The nebula is composed predominantly of hydrogen gas, which emits the pervasive red glow seen in this highly detailed featured image. The blue glow in the center is created by a trace amount of glowing oxygen. Young and massive stars located in the nebula’s center expel dust when they explode in supernovae. Eta Carinae, the most energetic star in the nebula’s center, was one of the brightest stars in the sky in the 1830s, but then faded dramatically. via NASA https://go.nasa.gov/2vFXMfD